GCSE Maths – Everything You Need to Know
GCSE Maths might be classed as one of the core subjects within the educative system in the United Kingdom, but more importantly, it’s an important skill set towards developing vital numerical and problem-solving skills. This overview will cover everything you need to know about GCSE Maths, from the core topics covered and grading system to effective studying techniques.
This blog it self is one of the best resources because we manage to get everything together. Revision resources, help from best tutors, past papers and more information which will give you full understanding of gcse math and help you with any question.
Key Topics in GCSE Maths

When studying for GCSE Maths, there are several key topics that students need to understand, each playing a vital role in developing a comprehensive grasp of mathematics. Here are some of the main areas:
Numbers
This topic delves into the fundamentals of numeracy, including integers, decimals, fractions, percentages, powers, roots, and the order of operations. It’s essential to have a solid understanding of these elements as they form the basis of more complex mathematical calculations.
- Integers and Place Value: Understanding whole numbers, decimals, and place value.
- Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages: Converting between them, and solving related problems.
- Powers and Roots: Calculating and manipulating squares, cubes, square roots, and cube roots.
- Ratio and Proportion: Solving problems involving proportional relationships.
Algebra
Algebra represents a significant leap for many students, introducing them to the concept of using symbols and letters to represent numbers and quantities in equations. This section includes topics such as simple equations, sequences, inequalities, and quadratic equations.
- Expressions and Equations: Simplifying expressions, solving linear equations and inequalities.
- Sequences: Understanding arithmetic and geometric sequences.
- Graphs: Plotting and interpreting linear and quadratic graphs.
- Quadratic Equations: Solving quadratics by factorisation, completing the square, and the quadratic formula.
Geometry and Measures
In this topic, students explore shapes, space, and measurements. They learn about angles, properties of 2D and 3D shapes, units of measurement, perimeter, area, volume, and transformations.
- Properties of Shapes: Understanding angles, lines, and properties of polygons.
- Transformations: Reflection, rotation, translation, and enlargement.
- Pythagoras’ Theorem and Trigonometry: Solving problems involving right-angled triangles.
- Perimeter, Area, and Volume: Calculating measurements of various shapes and solids.
Statistics and Probability
Statistics involves collecting, organising, and interpreting numerical data. Key topics include statistical measures (like mean, median, mode, and range), types of data, and data representation. Probability, on the other hand, deals with the likelihood of occurrence of different events, using concepts such as probability scales, theoretical probability, relative frequency, and tree diagrams.
- Data Handling: Collecting, representing, and interpreting data using charts and graphs.
- Probability: Calculating probabilities of single and combined events, including using probability trees.
Ratios, Proportions, and Rates of Change
This topic teaches students how to compare quantities, how things scale or grow, and the concept of constant rates of change. It involves ratios, proportionality, and direct and inverse proportion.
Each of these topics interlinks and helps build the larger mathematical picture. A strong understanding of these areas sets students up for tackling more complex mathematical problems and sets a strong foundation for future learning.
- Direct and Inverse Proportion: Solving problems and using graphs to illustrate proportional relationships.
- Rates of Change: Understanding gradients and interpreting real-life graphs.
Functions
Functions represent relationships where each input has a unique output, a key concept in mathematics. In GCSE Maths, you’ll learn to evaluate functions, interpret graphs, and work with types like linear and quadratic functions. Understanding functions helps solve mathematical problems and interpret real-world situations, building a foundation for advanced studies.
- Definition and Notation: Recognising functions as relationships with unique outputs for each input, using function notation like f (x).
- Evaluating Functions: Calculating outputs for given inputs by substituting values into function expressions.
- Interpreting Graphs: Understanding graphs of functions, identifying key features like intercepts and turning points.
- Types of Functions: Familiarity with linear, quadratic, and simple polynomial functions and their characteristics.
- Solving Problems: Using functions to solve real-world and mathematical problems, including setting up and solving equations.
- Composite and Inverse Functions: Understanding composite functions and finding inverses for simple functions.
Why Do Students Find GCSE Maths So Hard?
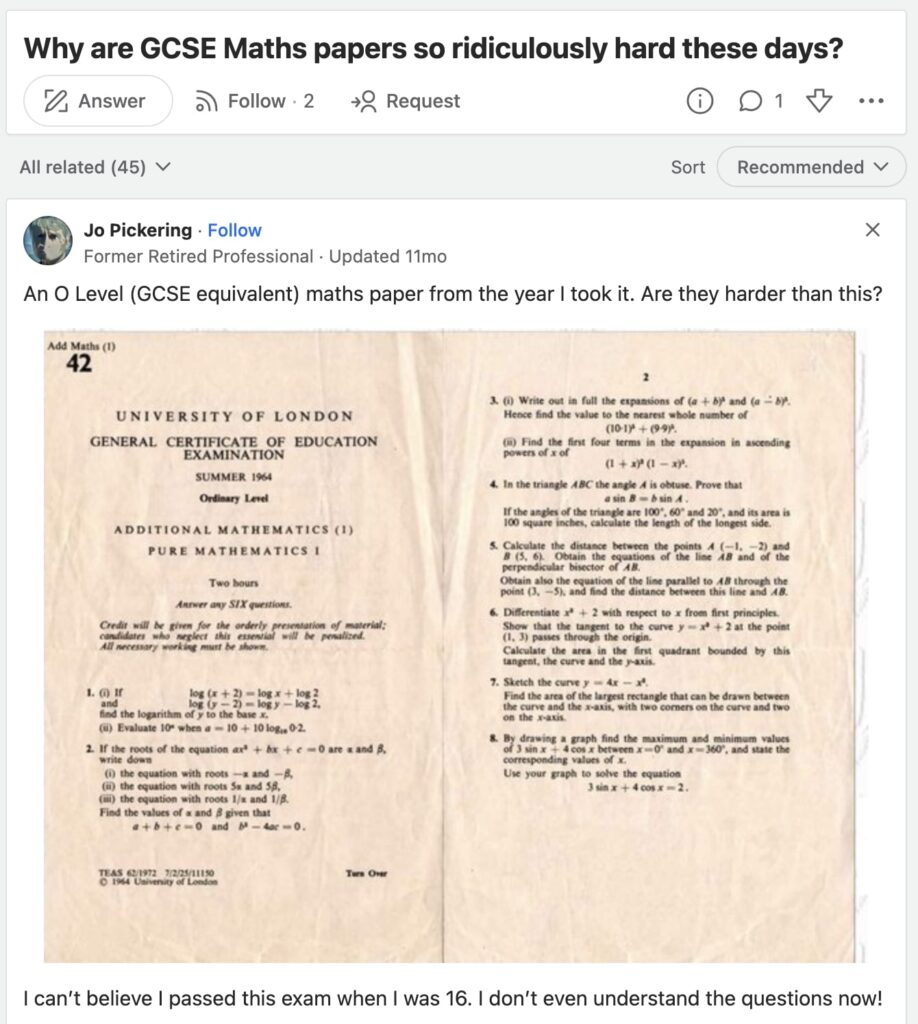
Even though every student’s experience with GCSE Maths may be unique, there are common challenges that many tend to face throughout their learning journey. Understanding these hurdles can help in identifying effective strategies to overcome them.
Understanding Abstract Concepts
Many students struggle with the abstract nature of certain mathematical concepts, particularly as they move from dealing with tangible quantities to symbolic representations in algebra. Grappling with ideas that can’t be visualised can be a significant obstacle for many learners.
Problem-Solving Under Time Pressure
GCSE Maths exams aren’t just a test of knowledge; they also challenge students’ ability to apply that knowledge swiftly and accurately. Managing time effectively while ensuring accuracy can be a tough balance to strike, leading to increased stress during exams.
Misconceptions and Gaps in Knowledge
Sometimes, misunderstandings or gaps in knowledge from earlier stages of education can hinder progress in GCSE Maths. As the subject builds on previously learnt concepts, a shaky foundation can make grasping new topics much more challenging.
Keeping Up with the Pace of Learning
The volume of material to be covered in GCSE Maths can be overwhelming. For some students, keeping up with the pace of teaching while fully understanding each topic can be a daunting task.
Lack of Confidence and Maths Anxiety
Maths can be intimidating, and a lack of confidence often leads to a self-perpetuating cycle of anxiety and underperformance. This mental hurdle can prove to be one of the biggest obstacles to success in GCSE Maths.
Recognising these challenges is the first step towards addressing them. The next sections of this guide will provide practical solutions and resources to help students conquer these common difficulties and thrive in their GCSE Maths journey.
Practicing with GCSE Maths Questios
Here are tips and examples of questions from past exams which will give you exact understanding of questions format. Moreover, we also provide answers with formulas and common mistakes done by lots of students. So for you to get better results you should understand also psychological moments which is provided as this common mistakes which you should work on before exams.
Question 1: Algebra
“Solve the equation 2x^2 – 5x – 3 = 0.”
Solution: This is a quadratic equation, and we can solve it using the quadratic formula x = [-b ± sqrt(b² – 4ac)] / 2a. Here, a=2, b=-5, and c=-3. Applying these values to the formula gives us the roots of the equation.
Common mistake: It’s essential to correctly identify the values of a, b, and c from the equation and ensure accurate calculation when using the quadratic formula.
Question 2: Geometry and Measures
“In a circle with a radius of 10 cm, find the length of the arc formed by a central angle of 60 degrees.”
Solution: To find the length of the arc, use the formula arc length = (θ/360) x 2πr, where θ is the central angle and r is the radius. Substituting θ=60 and r=10 into the formula will give the length of the arc.
Common mistake: Remember that the central angle should be in degrees when using this formula. Also, use the correct value of π.
Question 3: Statistics and Probability
“A bag contains 4 red, 3 blue and 2 green balls. One ball is drawn at random. What is the probability that it is neither red nor blue?”
Solution: The total number of balls is 4+3+2=9. The balls that are neither red nor blue are the green ones, of which there are 2. So, the probability is 2/9.
Common mistake: When calculating probability, ensure you’re considering the correct outcomes. The probability is defined as the number of desired outcomes divided by the total number of outcomes.
These questions offer a glimpse into the complexity and depth of GCSE Maths. Rigorous practice and understanding the underlying concepts are key to successfully answering such questions.
GCSE Maths Marking Scheme
Understanding the GCSE Maths marking scheme is essential for students to know exactly what examiners are looking for and how they can maximise their scores.
Structure of the GCSE Maths Marking Scheme

The marking scheme for GCSE Maths typically aligns with the areas of study: Number, Algebra, Geometry and Measures, Statistics and Probability, and Ratios, Proportions, and Rates of Change. Marks are allocated for each section according to their weight in the syllabus.
Marking for Accuracy and Method
Marks in GCSE Maths are usually awarded for two main aspects: the final answer and the method used. This means that even if a student gets the final answer wrong, they may still receive some marks if their method is correct. Similarly, an accurate answer with no clear method may not receive full marks.
Tiered Papers
GCSE Maths exams have two tiers: Foundation and Higher. The Foundation tier covers grades 1 to 5, while the Higher tier covers grades 4 to 9. The level of difficulty and the complexity of questions differ between these tiers.
Use of Marking Schemes in Revision
GCSE maths past papers and their respective marking schemes are invaluable resources for revision. They not only familiarise students with the format of the exam but also illustrate how marks are allocated. This helps students to understand how to approach each question strategically to gain the maximum marks possible.
Keep in mind, however, that while knowing the marking scheme is beneficial, truly excelling in GCSE Maths comes from a thorough understanding of the material and effective problem-solving skills.
Essential Tips for GCSE Maths Exam Day
Preparation is key to succeeding in any exam, but how you approach the actual exam day can make all the difference. Here are some essential tips to ensure that you perform your best during your GCSE Maths exam:
1. Get a Good Night’s Sleep
It may seem obvious, but many students underestimate the importance of sleep before an exam. A well-rested mind is better equipped to recall information, solve problems efficiently, and manage exam stress. Make sure to get at least 7-8 hours of sleep the night before to ensure you’re mentally alert and focused on the day of your exam.
2. Have a Balanced Breakfast
Start your day with a nutritious breakfast that provides long-lasting energy. Foods rich in complex carbohydrates and protein, such as whole grain cereal with milk or scrambled eggs with toast, can help sustain your energy levels throughout the exam. Avoid sugary foods that can cause an energy crash and leave you feeling sluggish midway through.
3. Double-Check Your Exam Essentials
Before leaving home, ensure you have everything you need for the exam:
- Exam Admission Slip: Check that you have your exam entry card and any other documentation required for entry.
- Stationery: Bring at least two pens (black or blue), pencils, a ruler, an eraser, a protractor, and a scientific calculator (if permitted).
- Calculator: Make sure your calculator is functioning properly and has fresh batteries. Check that it is approved for use in the exam and reset its memory beforehand.
- Water and Snacks: A bottle of water can keep you hydrated, and a light snack, such as a banana, can be helpful if permitted.
4. Arrive Early and Stay Calm
Give yourself plenty of time to get to the exam venue, aiming to arrive at least 30 minutes before the exam starts. This will allow you to settle in, find your seat, and have a few moments to relax. Avoid cramming in last-minute revision as it may increase anxiety—trust the preparation you’ve done so far.
5. Read the Instructions Carefully
As soon as you receive the exam paper, take a few minutes to read the instructions and understand what is being asked of you. Identify how many questions you need to answer, and whether there are specific sections that are compulsory. Misreading the instructions is a common mistake that can cost you valuable marks.
6. Allocate Your Time Wisely
Check how many questions you need to complete and divide your time accordingly. If a paper is 90 minutes long and there are 15 questions, allocate roughly 6 minutes per question. If you find yourself stuck on a difficult question, move on to the next one and come back later if time allows.
7. Show Your Workings Clearly
Always show your workings for each question, even if you think the answer is obvious. Not only does this demonstrate your problem-solving process, but it also means you may receive partial credit even if your final answer is incorrect. Additionally, if you have time at the end, you can review your calculations easily.
8. Review and Double-Check Your Answers
If you finish before time is up, use the remaining time to go back and review your answers. Check for careless mistakes, especially in calculations and written explanations. Make sure you have answered all the required questions and haven’t skipped any parts of multi-step problems.
9. Manage Exam Stress
It’s normal to feel nervous, but it’s important not to let stress overwhelm you. If you start feeling anxious, take a few deep breaths to calm down. Remember, a little stress can be beneficial as it keeps you alert, but too much can hinder your performance. Keep a positive mindset and remind yourself that you’ve prepared well.
10. Use All the Available Time
Even if you’ve answered all the questions, don’t leave early. Use every minute of the exam to review your answers, recheck your calculations, and ensure your responses are as complete as possible.
By following these tips, you can approach your GCSE Maths exam with confidence and perform at your best. Remember that preparation, time management, and a calm mindset are key components of exam success. Good luck!
How to Choose Between Foundation and Higher Tiers in GCSE Maths
Choosing the right tier for your GCSE Maths exam—Foundation Tier or Higher Tier—is crucial for maximising your potential and achieving the best possible grade. Each tier offers different levels of difficulty and affects the grades you can attain, so it’s essential to make an informed decision. Here’s a breakdown of what you need to consider:
Understanding the Differences
Foundation Tier: This tier covers grades 1-5 and focuses on core mathematical concepts and basic applications. It’s designed for students who find Maths challenging or who need to focus on mastering fundamental skills. The questions in the Foundation Tier are more straightforward, ensuring that students have a solid grasp of basic Maths topics, such as number operations, basic algebra, and geometry.
Higher Tier: This tier covers grades 4-9 and includes more complex and advanced topics. It’s suited for students who are confident in their Maths abilities and are aiming for higher grades, especially those considering further education in subjects like Maths, Science, or Engineering. The Higher Tier includes challenging questions that test problem-solving skills and require a deeper understanding of algebra, trigonometry, and other advanced topics.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Tier
Current Maths Ability: Assess your current level of understanding and confidence in Maths. If you are consistently achieving high grades and enjoy tackling complex problems, the Higher Tier is likely a better option. Conversely, if you struggle with some of the basic concepts, the Foundation Tier may be more suitable.
Future Academic and Career Goals: Consider how your GCSE Maths grade might impact your future plans. If you intend to pursue A-Level Maths or a degree in a Maths-related subject, achieving a higher grade is essential, and therefore the Higher Tier is more appropriate. For students not pursuing further Maths education, the Foundation Tier can provide a solid pass grade without the additional pressure of more difficult content.
Advice from Teachers: Your teachers will have a good understanding of your abilities and can provide valuable input. They may recommend a tier based on your performance in class, mock exams, and overall engagement with the subject.
Flexibility to Change Tiers: Schools typically make a preliminary decision on which tier students will sit, but this can often be adjusted as the exam date approaches. If you’re unsure, it’s worth discussing with your teachers whether switching tiers is possible closer to the exams, depending on your progress and confidence levels.
Impact on Overall Grades: Choosing the right tier can make a significant difference to your overall grade. For example, if you are taking the Foundation Tier, the highest grade you can achieve is a 5, which is equivalent to a high C/low B grade. On the other hand, the Higher Tier allows for grades up to 9, but you risk falling below grade 4 if you perform poorly, as the minimum grade achievable in the Higher Tier is 4.
GCSE Maths Revision

Revision is an essential part of preparing for GCSE exams, providing the opportunity to consolidate your knowledge and enhance your understanding of key concepts. Whether you’re new to the process or looking to refine your techniques, here’s how to make your GCSE revision both effective and engaging.
Understanding the Importance of Revision
Revision is more than just reviewing your notes; it’s about reinforcing your learning and identifying areas where you need improvement. For new students, it’s crucial to understand that effective revision can significantly impact your exam performance and build confidence. Experienced students can benefit from exploring new strategies to keep their revision dynamic and effective.
Creating a Personalised Study Plan
Start by developing a personalised study plan that reflects your learning style and academic goals. Identify the subjects and topics you need to focus on, and allocate time accordingly. Incorporate a mix of study methods, such as reading, writing summaries, and practising past papers. For experienced revisers, consider experimenting with advanced techniques like interleaving (mixing different topics in one study session) to enhance retention.
Using a Variety of Resources
Diversifying your resources can make revision more engaging and effective. In addition to textbooks and class notes, explore online resources like educational videos, interactive quizzes, and revision apps. New students should focus on building a solid foundation with these resources, while experienced students can seek out challenging materials to deepen their understanding.
Embracing Active Learning Techniques
Active learning involves engaging with the material in a way that promotes critical thinking and problem-solving. Techniques such as teaching concepts to others, discussing topics in study groups, and applying knowledge to real-world scenarios can enhance retention and comprehension. For those familiar with active learning, try incorporating techniques like mind mapping or creating flashcards to summarise key points.
Practising with Past Papers
Practising past exam papers is an excellent way to familiarise yourself with the exam format and assess your progress. For beginners, this helps in understanding the types of questions you might face. Experienced students can use past papers to refine their exam techniques and time management skills.
Effective Revision Resources for GCSE Maths
When it comes to revising for GCSE Maths, there’s a wealth of resources available to students. Ranging from websites and apps to forums and books, these tools can provide comprehensive coverage of the subject matter, aid in understanding complex concepts, and provide ample practice opportunities. Here’s a selection of some effective resources:
Websites
- BBC Bitesize: Offers a wide range of resources, including revision notes, quizzes, and practice questions covering the entire GCSE Maths syllabus.
- Corbettmaths: This site provides numerous practice papers, revision cards, and instructional videos.
- Maths Genie: Known for its vast collection of past papers along with corresponding solutions.
Apps
- GCSE Maths: Revision Questions: This app offers thousands of GCSE Maths revision questions, allowing students to practice extensively.
- Photomath: Helpful for understanding mathematical problems step-by-step. Users take a photo of a maths problem, and the app breaks it down into manageable steps.
YouTube Channels
- Khan Academy: Offers easy-to-understand video tutorials on a wide range of GCSE Maths topics.
- HegartyMaths: Created by an experienced Maths teacher, this channel offers comprehensive video lessons on all topics in GCSE Maths.
Forums
- The Student Room: A forum where students can discuss topics, share revision tips, and get advice from peers.
Books
- GCSE Maths AQA Revision Guide: A comprehensive revision guide with clear explanations, worked examples, and practice questions.
- New GCSE Maths Edexcel Revision Book: Provides a detailed coverage of the Edexcel specification, with numerous practice questions.
These resources cater to different learning styles, allowing students to choose what works best for them. Remember, the goal is not to use all resources, but rather to find the ones that match individual learning styles and preferences. Successful revision involves consistency, practice, and an understanding of core concepts.
Further Maths GCSE offers a challenging extension to standard GCSE Maths, ideal for students with a strong interest in mathematics or those considering advanced studies. Here’s how to prepare and what to expect:
Further Maths GCSE

Further Maths GCSE offers a challenging extension to standard GCSE Maths, ideal for students with a strong interest in mathematics or those considering advanced studies. Here’s how to prepare and what to expect:
- Foundation in GCSE Maths: Ensure a strong grasp of core GCSE Maths topics, as Further Maths builds on these principles.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Develop advanced analytical and problem-solving skills by tackling challenging problems.
- Mathematical Notation: Familiarise yourself with advanced mathematical notation and symbols.
Key Topics in Further Maths GCSE
- Algebra and Functions: Advanced algebraic expressions and functions.
- Geometry and Trigonometry: Complex geometric concepts and trigonometric identities.
- Calculus: Basics of differentiation and integration.
- Matrices: Matrix operations and applications.
- Complex Numbers: Introduction to imaginary numbers.
- Probability and Statistics: In-depth study of probability distributions and statistical methods.
Differences Between GCSE Maths and Further Maths GCSE
- Depth and Complexity: Further Maths covers more complex topics and requires deeper problem-solving skills.
- Preparation for Advanced Studies: Bridges the gap to A-level Maths, ideal for future STEM studies.
- Assessment Structure: More challenging exams with a focus on detailed reasoning.
Further Maths GCSE is an excellent opportunity for students to deepen their mathematical understanding and prepare for future academic challenges.
The Advantages of Online GCSE Maths Tutoring
There are a lot of benefits to online tutoring – from gaining academic assistance from the comfort of their own home. The advantages of online tutoring include:
- No travel time or adjusting schedules to meet in-person.
- Tutors tailor their teaching style to the individual student’s needs, promoting a deeper understanding of the subject.
- Regardless of their location, students can receive quality tutoring from anywhere in the UK.
- Digital whiteboards, screen sharing, video conferencing, and other tech tools enhance the learning experience.
- Online platforms often provide tools for record-keeping and progress tracking, making it easier for students and parents to monitor progress.
Become a Maths Expert with Edumentors
In today’s dynamic educational landscape, academic excellence increasingly hinges on tailored, adaptive learning experiences. This is particularly true for GCSE Maths, a fundamental stepping stone for both academic and career aspirations. Mastery of this subject goes beyond mere understanding; it involves a deep, practical grasp of mathematical concepts.
Edumentors stands out in facilitating this level of mastery. It transcends traditional tutoring by transforming complex mathematical ideas into engaging, solvable challenges. This approach turns learning into an intellectually stimulating experience.
The strength of Edumentors lies in its team of GCSE maths tutors. These individuals are not only experts in their field, having distinguished themselves academically at leading UK universities, but they also bring a palpable passion and commitment to teaching. They serve as mentors, inspiring a robust understanding of maths and instilling confidence across a diverse range of learners.
For anyone on the path to GCSE Maths proficiency, Edumentors presents a compelling option for achieving excellence in this crucial subject.








