GCSE Mark Schemes and Examiner Reports Explained
As a GCSE student, you’ve probably heard the phrase “learn the mark schemes” more times than you care to count 🙄. But do you really know what it means, or how to use mark schemes to your advantage? Let’s dive into the world of GCSE mark schemes and examiner’s reports, and show you how understanding them can help with your revision.
One of the most valuable things you can do when preparing for exams is to practice with past papers. But it’s not just a matter of answering the questions and hoping for the best. By familiarising yourself with the mark schemes and examiner’s reports, you can learn how to grade your own work and gain insight into your strengths and weaknesses. This, in turn, can help you focus your revision efforts and improve your chances of success. So, let’s get started!
Overview of GCSE Mark Schemes
GCSE mark schemes are the criteria that examiners use to grade students’ answers in exams. They are made up of a set of descriptors that outline what is required for a student to achieve each grade. Then, grade boundaries determine which grade the student gets.
Each GCSE subject has its own set of mark schemes, which are developed by the exam board that oversees that subject. These mark schemes take into account the specific content and skills required for that subject, and they are updated regularly to reflect any changes to the syllabus.
For instance, this is what the mark scheme for Edexcel GCSE Maths higher tier (paper 1) looks like:
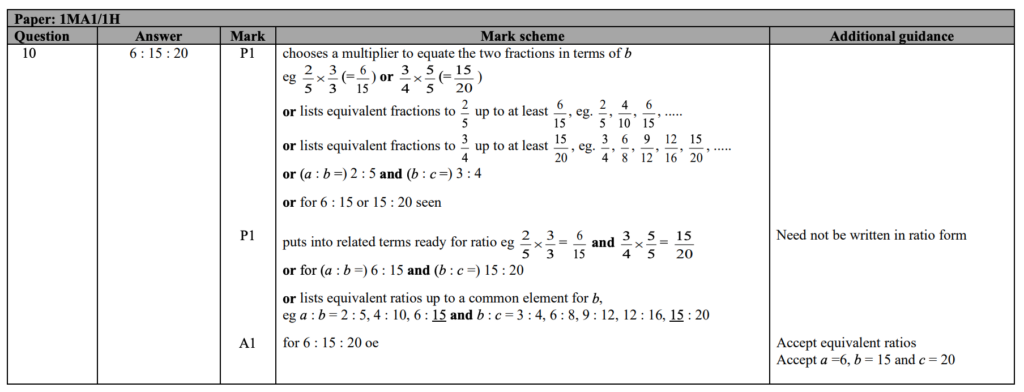
Here is what a part of a mark scheme looks like for essays (AQA GCSE English Language paper 1):
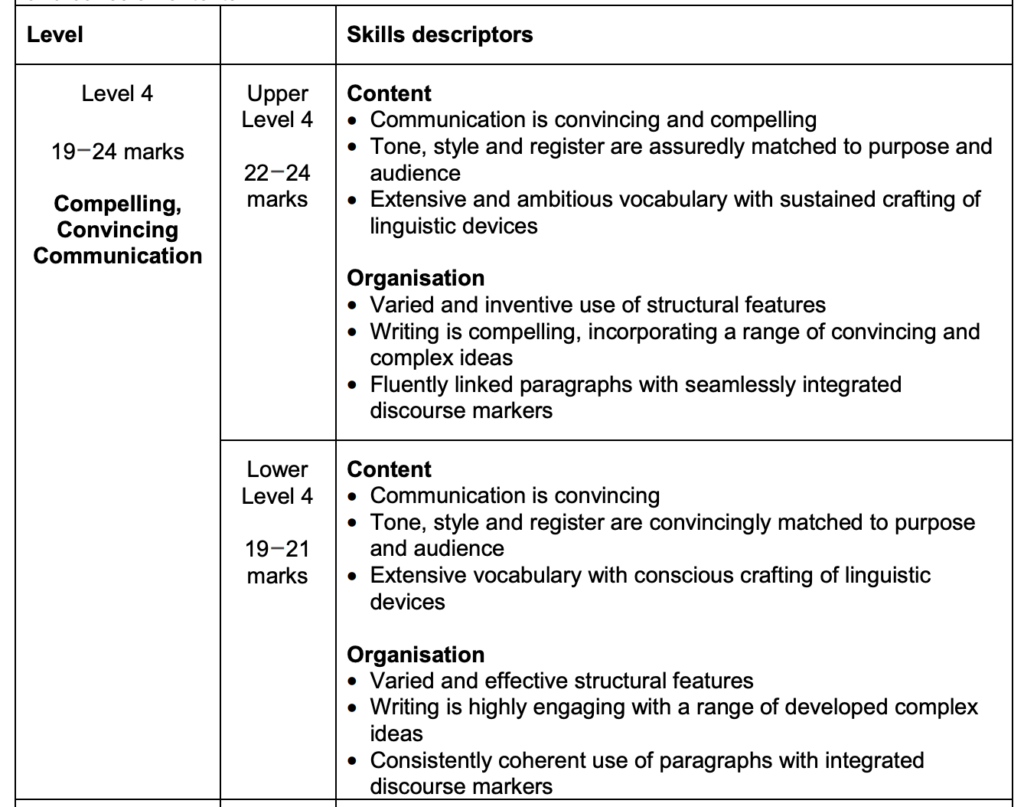
It’s important for GCSE students to understand the mark schemes for their subjects, as it can help them to identify their strengths and weaknesses in each topic. By reviewing your past exam papers using the mark scheme, you can see where you gained marks and where you lost them and can use this information to focus your revision on areas where you need to improve.
In addition, understanding the mark scheme can help you to write better answers in exams, as you will have a clearer understanding of what the examiners are looking for. You can use the mark scheme to structure your answers and ensure that you are including all of the key points required to achieve the higher grades.
Assessment Objectives (AOs) Explained
Assessment Objectives (AOs) are used in the mark schemes of GCSE exams to evaluate how well students have understood and demonstrated their knowledge of the subject. There are usually four or five AOs in each subject, and each one focuses on a different aspect of the subject knowledge or skill.
Here’s a breakdown of the different AOs and what they mean:
- 📌 AO1 – Knowledge and understanding – This AO is about how well a student can recall and explain the key concepts and ideas in the subject. This includes demonstrating an understanding of key terms, theories, and concepts.
- 📌 AO2 – Application of knowledge and understanding – This AO is about how well a student can apply their knowledge and understanding to solve problems or answer questions. This includes demonstrating the ability to analyse, interpret, and evaluate information.
- 📌 AO3 – Analysis and evaluation – This AO is about how well a student can critically analyze and evaluate information, arguments, and evidence in the subject. This includes demonstrating the ability to make judgments and draw conclusions.
- 📌 AO4 – Synthesis and creativity – This AO is about how well a student can synthesize and create new ideas or solutions based on their knowledge and understanding of the subject. This includes demonstrating the ability to use creativity and imagination to solve problems or answer questions.
It’s important for you to understand these different AOs because you will be assessed on each of them in your GCSE exams. By focusing on improving your skills in each AO, you can improve your overall grades and performance in the subject.
How Do Assessment Objectives Vary Between Subjects?
The objectives (AOs) vary between different subjects as they are tailored to suit the specific requirements of each subject.
For example, in an English Language GCSE exam, AO1 (read, understand and respond to texts) and AO2 (analyse language and structure) may be more prominent, while in a Maths GCSE exam, AO1 (use and apply standard techniques) and AO2 (reason, interpret and communicate mathematically) may be more emphasised. Therefore, it is important to check the specific AO requirements for the subject you are studying to ensure you are fully prepared for the exam.
How Do Assessment Objectives Vary Between Exam Boards?
While the general principles of the assessment objectives are similar across different exam boards, there may be some differences in how they are applied and weighted in each subject. For example, in English Language, AO1 (content and organisation) and AO2 (language, form and structure) are given equal weightings in both AQA and Edexcel. However, in OCR, AO2 carries a higher weighting than AO1.
Similarly, in Mathematics, AO1 (recall and use of knowledge) and AO2 (mathematical arguments, language and proof) are given equal weightings in AQA, but in Edexcel, AO2 is weighted more heavily than AO1.
It is important for students to be aware of these variations in the assessment objectives across different exam boards when preparing for their exams, as they may need to adjust their revision strategies accordingly. They should also familiarise themselves with the specific mark schemes and examiner’s reports provided by their exam board to understand how the assessment objectives are applied in practice.
Understanding Examiner’s Reports
Another useful resource for students is the examiner’s reports, which are published by the exam boards after each exam series. These reports provide detailed feedback on the performance of students in the exams, highlighting common strengths and weaknesses and providing guidance on how to improve.
Examiner’s reports can be particularly helpful in identifying areas where students may have struggled, or where they could have gained additional marks. For example, an examiner’s report might highlight that many students struggled with a particular question or topic, and provide guidance on how to approach similar questions in the future.

It’s important to note that examiner’s reports can vary significantly between exam boards. While the underlying assessment objectives may be similar, each board may have slightly different expectations in terms of the level of detail required in answers, or the emphasis placed on certain aspects of the syllabus. As a result, it’s a good idea to consult the examiner’s reports for the specific exam board you are studying with, rather than relying on reports from other boards.
Tips for Using Mark Schemes and Examiner’s Reports
✅ Familiarise Yourself with the Mark Scheme and Examiner’s Reports

To use these resources effectively, you need to have a good understanding of them. Take some time to read through the mark scheme and examiner’s reports for your subjects, paying attention to the assessment objectives and the types of responses that are awarded marks.
✅ Grade Your Own Papers
One of the most useful things you can do with a mark scheme is to grade your own past papers. This will help you identify your strengths and weaknesses and give you an idea of what areas you need to focus on when revising. However, there are also tools like MarkMyGCSE that can grade the paper for you and give you useful feedback on how to improve according to the mark schemes and examiner reports.
✅ Look for Patterns in the Examiner’s Reports
Examiner’s reports often highlight common mistakes or areas where students struggled. Pay attention to these patterns and try to avoid making the same mistakes yourself. Look for guidance on how to improve your performance in those areas.
✅ Use the Mark Scheme as a Revision Tool
Mark schemes can be used as a revision tool to help you understand what examiners are looking for. Use them to create practice questions and test yourself on how well you understand the material.
✅ Don’t Rely Solely on the Mark Scheme
While mark schemes are helpful, they shouldn’t be the only thing you rely on when revising. Make sure you understand the material thoroughly and can apply it in different contexts.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding GCSE mark schemes and examiner’s reports can provide you with valuable insights into your performance and guide you towards achieving better results. By using mark schemes and examiner’s reports as tools for self-assessment, you can identify your strengths and weaknesses, target areas for improvement, and ultimately improve your grades.
It’s important to keep in mind that while mark schemes and examiner’s reports follow a general framework across different subjects and exam boards, there may be slight variations that students should be aware of. Therefore, it’s always a good idea to familiarise yourself with the specific mark scheme and examiner’s report for the subject and exam board you are studying.
Finally, for students looking to practice using mark schemes and examiner’s reports, past papers are an excellent resource. They can be found on various websites, including Edumentors, which provides a wide range of free past papers for GCSE students. So, make use of this resource and put your knowledge of mark schemes and examiner’s reports into practice!
If you need additional help understanding mark schemes or examiner reports, Edumentors tutors are there for you to help!








