The national curriculum in England and Wales is meticulously designed to provide a structured and balanced education for all students. This comprehensive guide delves into each key stage, revealing the intricacies of the curriculum and offering insights into how each stage prepares students for their educational journey and beyond.
What are the Key Stages?
The national curriculum is segmented into distinct phases known as key stages, each tailored to the developmental stage and learning needs of students. These stages ensure that from an early age, students gain access to a broad and diverse education, setting a solid foundation for lifelong learning and achievement. Here is a quick look at all the key stages:
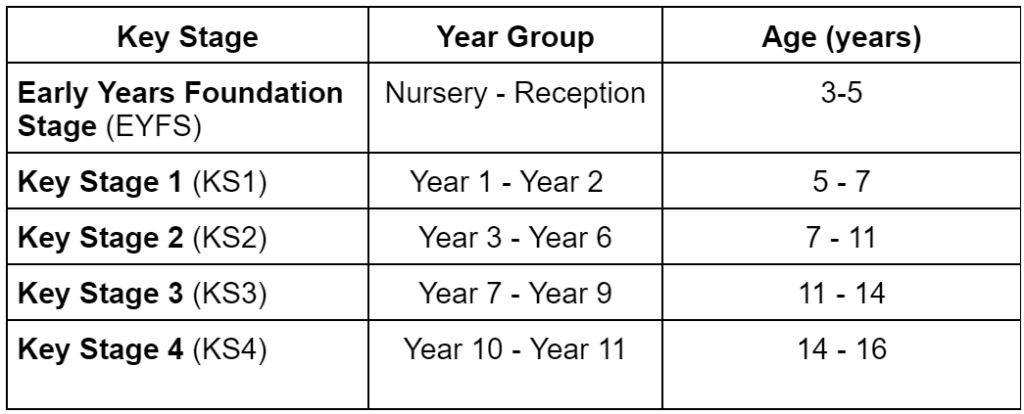
Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS) – Ages 3-5
The EYFS is the first step in the national curriculum, focusing on learning through play and interactive activities. It’s designed to nurture an early love for learning in a supportive environment. The curriculum covers six critical areas:
- Personal, Social, and Emotional Development -This area aims to develop children’s confidence, emotional well-being, and ability to form healthy relationships.
- Communication, Language, and Literacy – Fundamental to early childhood development, this focuses on developing children’s spoken language, early reading, and writing skills.
- Mathematical Development – Introduces basic concepts of numbers, counting, and simple calculations, fostering problem-solving skills.
- Understanding the World – Encourages children to make sense of their physical world and their community through exploration, observation, and learning about people and places.
- Physical Development – Focuses on improving children’s coordination, control, manipulation, and movement. It also helps them understand the importance of physical activity and making healthy food choices.
- Creative Development – Enables children to explore and play with a wide range of media and materials, encouraging creativity, imagination, and the ability to express themselves artistically.
Key Stage 1 – Ages 5-7
Key Stage 1 builds on the foundation laid during the EYFS, with a greater focus on formal learning. It introduces more structured education but maintains an emphasis on learning through play and exploration.
- Core Subjects – English, Maths, and Science are the core focus, with students beginning to develop fundamental skills in reading, writing, arithmetic, and basic scientific understanding.
- Assessments – The culmination of Key Stage 1 sees students taking the Standard Assessment Tests (SATs), which evaluate their knowledge in core subjects. The assessment results help teachers understand the students’ needs and tailor their teaching methods accordingly.
Key Stage 2 – Ages 7-11
This stage is critical for consolidating the basic skills learned in Key Stage 1 and expanding into more complex subjects and concepts.
- Curriculum Expansion – In addition to core subjects, students are introduced to a wider curriculum including history, geography, modern foreign languages, and computing, broadening their knowledge and understanding of the world.
- Assessments -SATs at the end of Year 6 are more comprehensive, covering English reading, English grammar, punctuation and spelling, maths, and science. These results are important indicators of a student’s academic progress and readiness for secondary education.
Key Stage 3 – Ages 11-14
Transitioning into secondary education, Key Stage 3 offers a broader curriculum designed to explore students’ interests and abilities in a wide range of subjects.
- Subject Choices – Students study a broad curriculum that includes the arts, design and technology, citizenship, physical education, and more, in addition to the core subjects. This variety helps students to identify their interests and strengths as they begin to consider their GCSE options.
- Preparation for Key Stage 4 – The final year of Key Stage 3 involves choosing which subjects to pursue at GCSE. This decision-making process is crucial, as it influences students’ future academic and career paths.
Key Stage 4 – Ages 14-16
Key Stage 4 focuses on preparing students for their General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) exams, which are a gateway to further education and employment opportunities.
- GCSE Exams – Students typically select 8-10 subjects for their GCSEs, including compulsory subjects such as English, Maths, and Science. The choices made at this stage can significantly impact future study and career opportunities.
- Further Education and Career Planning – Key Stage 4 is not only about preparing for exams but also about starting to plan for further education and career paths. Schools often provide career guidance to help students make informed decisions about their futures.
National Curriculum Aims and Expectations
Each key stage is underpinned by specific aims and expectations, detailing the knowledge, skills, and understanding that students should achieve. Adherence to these aims ensures a consistent and high-quality education for all students, equipping them with the necessary tools for success in their subsequent educational endeavours and beyond.
Why You Might Want to Consider Private tutoring?
Private tutoring has become an increasingly popular option for parents looking to support their children’s education. Various factors motivate parents to consider private tutoring for their children, ranging from enhancing academic achievement to personalising learning experiences. Setting the foundation for a successful academic life is crucial, as it sets a good starting point for your child’s academic future and is a long-term investment, with this said, Edumentors tutors are the market-favorite for their extremely personalised approach with professional student-tutors from UK’s top universities that can offer first-hand insight and knowledge into what it takes to be a successful student.
1. Personalised Learning Approach
Private tutoring offers tailored learning experiences that address the individual needs, strengths, and weaknesses of a student. This personalised approach can be particularly beneficial for students who may not thrive in the one-size-fits-all approach often found in classroom settings.
2. Flexible Scheduling
Tutoring can often be scheduled around the family’s routine, providing flexibility that is not available in traditional school settings. This convenience allows tutoring sessions to be arranged at times that are most effective for the student’s learning and family commitments.
3. Boost Academic Performance
Parents may seek private tutors to help improve their children’s grades and academic performance. Tutors can provide targeted support in specific subjects where students may be struggling or need extra help to excel.
4. Preparation for Exams
Tutoring is often sought to prepare for specific exams, such as SATs, GCSEs, A-levels, or entrance exams for selective schools. Tutors can offer specialised knowledge and exam preparation techniques that can significantly improve a student’s performance.
5. Enhance Confidence and Self-esteem
Personalised attention from a tutor can help build a student’s confidence in their abilities. This increased self-esteem can translate into a more positive attitude towards learning and schoolwork.
6. Support for Specific Learning Needs
Children with special educational needs (SEN), such as dyslexia or ADHD, can greatly benefit from the one-on-one attention and tailored strategies that private tutoring provides. Tutors with experience in SEN can offer approaches that might not be extensively available in regular classrooms.
7. Develop Study and Time Management Skills
Tutors can teach students effective study techniques and time management strategies that are not only beneficial for their current academic pursuits but also valuable life skills.
Conclusion
Understanding the structure and objectives of each key stage within the national curriculum is essential for supporting students’ educational journey. By providing a clear framework and progression path, the national curriculum ensures that students in England and Wales receive a comprehensive and fulfilling education, laying the groundwork for lifelong learning and success.









