Wave speed equation is an important concept in physics that helps us understand how waves travel through different mediums. Whether it’s sound waves, water waves, or light waves, knowing their speed is essential for studying their behaviour. But what is the equation for wave speed? The wave speed formula is:
Also, this equation shows that the speed of a wave depends on its wavelength (the distance between two peaks) and its frequency (the number of waves passing a point per second).
So, if you’re wondering how to find the speed of a wave, simply multiply these two values together. Understanding this equation is useful in many areas of science, from predicting ocean waves to analysing sound waves in music.
Understanding the Wave Speed Formula
In fact, the wave speed equation helps us understand how waves move through different mediums. It is written as: v = f × λ
This wave speed formula shows that wave speed depends on two important factors: wavelength and frequency.
- Wavelength – This is the distance between two consecutive wave peaks or troughs. It is measured in metres (m). The wavelength equation helps calculate this value in different wave types.
- Frequency – This refers to how many waves pass a fixed point in one second. It is measured in hertz (Hz).
- Speed – This is how fast the wave travels through a medium. It is usually measured in metres per second (m/s).
Additionally, the equation for wave speed shows that if the wavelength increases, the frequency must decrease to keep the speed constant. Similarly, if the frequency increases, the wavelength must decrease. This relationship explains why sound travels at different speeds in air, water, and solids.
Thus, by understanding the wavelength equation and the wave speed formula, you can calculate wave speed in real-world situations, such as sound waves in air or ocean waves at the beach.
The Wave Speed Triangle
Besides, the wave speed triangle is a simple tool that helps you remember the relationship between wave speed, wavelength, and frequency. So, if you struggle with rearranging formulas, this visual represantiation makes calculations easier.
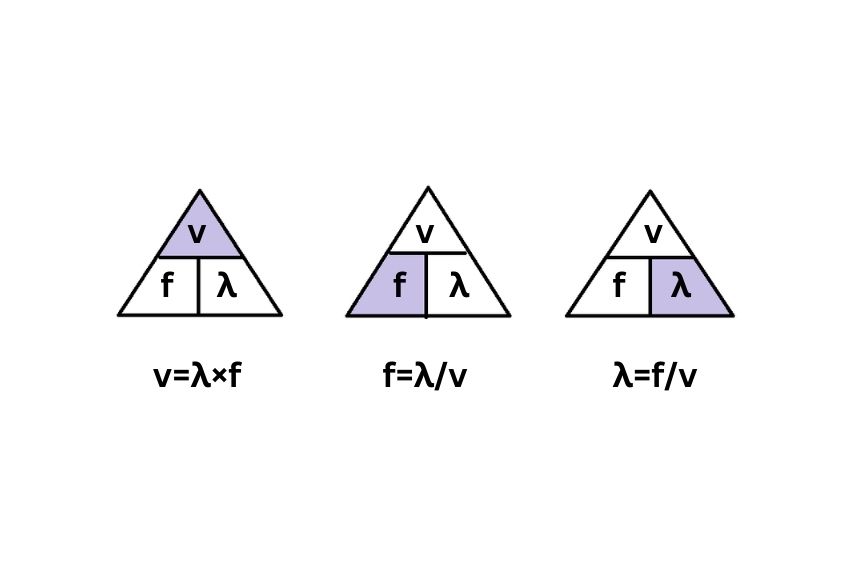
How to find the speed of a wave – λ × f (wavelength × frequency).
How to find wavelength – v ÷ f (wave speed ÷ frequency).
And to find frequency – v ÷ λ (wave speed ÷ wavelength).
As a result, using the wave speed triangle makes solving equations simple. Whether calculating sound waves, water waves, or light waves, this trick helps you rearrange the wave speed equation quickly.
Practical Applications of the Wave Speed Equation
In reality, the wave speed equation is not just a formula used in physics textbooks. It applies to many real-world situations, helping scientists and engineers understand how waves behave. From sound waves to light waves and ocean waves, calculating wave speed is essential in various fields.
Real-World Uses of the Wave Speed Equation
Sound Waves – The speed of sound varies depending on the medium. In air, it travels at about 343 m/s, while in water, it moves faster. This explains why underwater sounds reach our ears more quickly than in the air.
Light Waves – Light waves travel at an incredible speed of 300,000,000 m/s in a vacuum. Using the wavelength equation, scientists can study different types of light, from infrared to ultraviolet, to understand the universe.
Water Waves – Oceanographers use the wave speed formula to predict the movement of ocean waves. By calculating wavelength and wave speed, they can forecast tsunamis and design safe coastal structures.
How to find the Speed of a Wave: Example
A wave in the ocean has a wavelength of 5 meters and a frequency of 2 Hz. What is its wave speed?
Solution:
Using the wave speed equation:
The wave speed is 10 meters per second.
Consequently, understanding wave speed helps in many scientific applications, from engineering soundproof rooms to improving radio signals. By applying this knowledge, we can solve real-world problems and improve technology.
Avoiding Mistakes When Using the Wave Speed Equation
The wave speed equation is simple, but many students make common mistakes when using it. Hence, understanding these errors can help you avoid confusion and get accurate answers.
Misconception 1: Mixing Up Wave Speed Equation Units
On the other hand, one of the biggest mistakes is using the wrong units. Wavelength should always be in meters (m), frequency in hertz (Hz), and wave speed in meters per second (m/s). If you use centimeters or kilohertz, you must first convert them to standard units.
Misconception 2: Forgetting to Rearrange the Wave Speed Equation
Also, many students struggle with rearranging the equation. If you’re asked how to find the speed of a wave, remember that wave speed equals wavelength × frequency. But if you need to find wavelength or frequency, divide wave speed by the known value.
Misconception 3: Assuming Wave Speed is Always the Same
Different waves travel at different speeds depending on the medium. For example:
Sound waves move faster in solids than in air.
Light waves slow down when passing through water or glass.
Water waves are affected by depth and wind speed.
Tips For Succesfull Calculations
- Double-check your units before solving the equation.
- Use the wave speed triangle to rearrange the formula correctly.
- Consider the medium the wave is traveling through—speed is not always constant.
- Practice with real-world examples to build confidence in solving wave speed problems.
- Use a formula sheet to quickly recall equations and avoid mistakes during exams.
Finally, by understanding what the equation for wave speed represents and using the right approach, you can avoid mistakes and solve problems with confidence.

Advanced Considerations: How Mediums and Conditions Affect Wave Speed
The wave speed equation applies to all types of waves, but the speed of a wave can change depending on the medium it travels through. Understanding these variations is essential for accurately predicting wave behaviour in real-world scenarios.
How Mediums Affect Wave Speed Equation
waves move at different speeds depending on whether they travel through solids, liquids, or gases.
Sound Waves: Travel fastest in solids, slower in liquids, and slowest in gases because particle density affects how vibrations pass through a medium.
Light Waves: Move fastest in a vacuum but slow down in air, water, or glass due to interactions with particles.
Water Waves: Change speed depending on depth—deeper water allows waves to travel faster.
Wave Dispersion and Its Effects on Wave Speed
Wave dispersion occurs when different wavelengths of a wave travel at different speeds in the same medium. This is common in water waves and light waves.
- In ocean waves, longer wavelengths travel faster than shorter ones, affecting how waves spread over long distances.
- In light waves, dispersion explains why a prism splits white light into a spectrum—different wavelengths bend at different angles.
How to Find the Speed of a Wave in Different Conditions
Accordingly, by using the equation for wave speed, you can calculate wave motion in different mediums. However, factors like temperature, pressure, and density must also be considered. For example, xcientists and engineers use advanced calculations based on the wavelength equation to improve designs for optics, communication systems, and underwater exploration.
By understanding these advanced considerations about wave relationships, you can see why the wave speed equation is more than just a formula—it helps explain how waves behave in complex environments.
Conclusion
Thus ,understanding the wave speed equation is essential for studying how waves move through different mediums. Whether it’s sound waves, light waves, or water waves, knowing how to find the speed of a wave helps in many scientific and practical applications.
Moreover, we explored the wave speed formula and how it relates wavelength and frequency. We also discussed the wave speed triangle, a simple tool for solving equations, and how this concept applies in real-world situations, from ocean waves to light waves. Common mistakes when using the wave speed equation were highlighted, along with advanced topics like wave dispersion and how different mediums affect the speed of a wave.
In addition, students who need extra support, online physics tutors can provide personalised guidance to help master wave calculations with confidence. So, If you’re ready to improve your understanding of wave speed and other physics concepts, explore expert physics tutoring today and take your learning to the next level!
FAQs:
How to find wave speed?
To find wave speed, use the wave speed equation:
Wave Speed=Wavelength×Frequency
Simply multiply the wavelength (λ) by the frequency (f) to get the wave speed in meters per second (m/s).
How to calculate wave speed without wavelength?
If wavelength is unknown, you can still calculate wave speed using: Distance and time:
Also, if you know how far a wave has traveled and how long it took, you can find its speed.
Alternative formulas in specific cases:
For sound waves, use speed of sound in a given medium (e.g., 343 m/s in air).
For light waves, use speed of light (3.0 × 10⁸ m/s).
What equation links frequency, wavelength, and wave speed?
The equation linking these three variables is:
v = f × λ
This formula shows that wave speed is directly proportional to both frequency and wavelength. If one increases while the speed remains constant, the other must decrease.
How to calculate the speed of a progressive wave?
A progressive wave is a wave that moves energy from one place to another. To calculate its speed, use: v = f × λ
If either the wavelength or frequency is missing, you may need additional information about the medium or time taken for the wave to travel a certain distance.
What is the speed equation for GCSE physics?
For GCSE physics, the standard wave speed equation is: v = f × λ
where v is wave speed (m/s), f is frequency (Hz), and λ is wavelength (m). This equation is used for all types of waves, including sound, water, and light waves.








