New GCSE Grades & Sixth Form: What Changed + A-levels Path
Table of Contents:
- What is a Sixth Form (6th form)?
- Which GCSEs Should You Do to Get into Sixth Form (6th form)?
- What Grades Do You Need to Get into a Sixth Form (6th form)?
- The New GCSE Grades System
- How to Apply to Sixth Forms?
- How to Know if Your Sixth Form (6th form) is Good?
- What Happens If You Don’t Get Accepted into Sixth Form (6th form)?
- To Sum Up
What is a Sixth Form (6th form)?
So, whats a sixth form? The sixth form (6th form) is a college that specifically caters to students who have completed their GCSEs. They offer A-Levels, BTECs and other qualifications which allow young people to continue their studies leading up to university or higher education.
So, why is it called Sixth Form? A Sixth Form differs from other parts of your education because it can be more flexible and less structured than primary or secondary school. You’ll have more freedom to choose what you want to study, so if there are certain subjects or classes that interest you, this is an ideal time to explore them further.
If you’re considering Sixth Form (6th form) after completing your GCSEs, you should know that the courses tend to be more challenging than what you might have experienced during your GCSE years. One great thing about Sixth Form (6th form) is that you have complete freedom to choose the subjects you want to study. No longer are you restricted to a set of core subjects, you can pick and choose based on what you need to pursue your desired university path.
Which GCSEs Should You Do to Get into Sixth Form (6th form)?
A good grasp of GCSEs is essential to getting into sixth form (6th form), but it’s also important to consider which GCSEs you take.
As well as core subjects such as English and Mathematics, there are many other courses available that you can choose from at your school or college. For example, if you enjoy art or drama then these subjects may be suitable for you. You could even study a foreign language like French or German if you want to learn something new!
If one of these options sounds appealing, then talk to your teachers about which GCSEs are suitable for the course that interests you most. In some cases, though, it’s worth checking out what grades are needed from students, including how they might impact your chances based on the university acceptance rate, before making any decisions about future plans.
What Grades Do You Need to Get into a Sixth Form (6th form)?
Admission to Sixth Form (6th form) can be competitive, with entry requirements varying depending on the school or college.
How Many GCSEs Do You Need for A-levels?
Most schools require a minimum of 4 GCSEs at grade C or above. Additionally, good grades in your chosen subjects for A-level study. For example, if you want to study English in Sixth Form (6th form), you may need to have a grade B in both English and Maths.
In addition to the academic requirements, some Sixth Forms may also require applicants to attend an interview or assessment day. This is to ensure that the student is suitable for the course they are applying for and to assess their suitability.
It is important to check with each individual school for their specific requirements. They may have different expectations based on past applicants and their own admission standards.
Good GCSE grades are crucial for gaining acceptance into Sixth Form (6th form), so it is essential to put in the effort to achieve the best possible grades. This can be achieved by working hard, seeking extra help from teachers or parents, practicing good revision techniques, and remaining calm during exams. Improving your grades can increase your chances of being accepted into the Sixth Form (6th form) of your choice.
Do Sixth Forms Look at Mock Grades?
Yes, sixth forms sometimes do look at mock grades. Many Sixth Forms may require you to submit your mock exam results as part of your application. The purpose of this is to give the institution an idea of your academic potential. It is therefore important to ensure that you have taken the necessary steps to achieve your best in your mock exams.
It is important to remember that mock grades are not always indicative of your final grades, as they are not always taken under the same conditions as the real exams. However, they can still be useful for Sixth Forms to assess your academic potential. Therefore, it is important to take your mock exams seriously and to put in the necessary effort.
The New GCSE Grades System
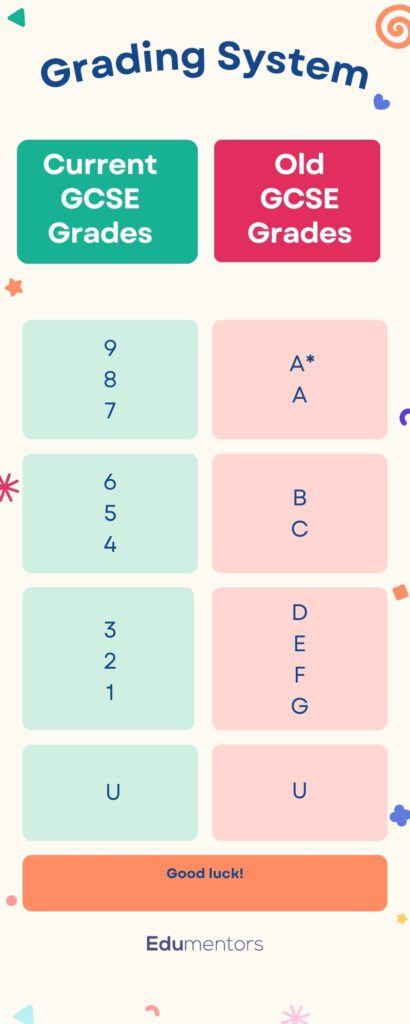
The introduction of the 9-1 grading scale for GCSEs represents a significant shift from the traditional A*-G system. This change, part of a wider curriculum reform in England, seeks to introduce a more rigorous assessment method, aiming to better distinguish student achievements, particularly at the higher end of the academic spectrum.
Understanding the 9-1 Scale
Under the new grading system, 9 is the highest grade, reflecting exceptional achievement, while 1 is the lowest. This new scale is designed to provide more differentiation among high-performing students, with the top GCSE grades (7-9) set apart to distinguish levels of excellence that were previously grouped under the A and A* categories. The rationale behind this differentiation is clear – Grade 9 is awarded to roughly the top 20% of students achieving a grade 7 or above, celebrating exceptional performance that surpasses the old A* grade.
Comparing Old and New GCSE grading
Transitioning from the A*-G to the 9-1 grading system is not a direct conversion but rather a reimagining of how student achievement is classified. GCSE grades 4-6 under the new system encapsulate the broad middle range previously covered by B and C grades, with GCSE grade 4 designated as a standard pass, analogous to the old GCSE grade C. This benchmark is critical, as it remains a minimum requirement for progression to further education or employment in many fields. The introduction of a GCSE grade 5 as a strong pass further underscores the heightened expectations placed on students, aiming to align English educational standards with those of other high-performing countries.
- Grade 9: Above A*
- Grade 8: Between A* and A
- Grade 7: Equal to A
- Grade 6: Just above B
- Grade 5: Between B and C
- Grade 4: Equal to C
- Grade 3: Between D and E
- Grade 2: Between E and F
- Grade 1: Between F and G
The Purpose Behind the 9-1 Grading Shift?
The shift to the 9-1 GCSE grading system is part of a broader educational reform aimed at making GCSEs more challenging. The move towards linear assessment, with less emphasis on coursework, and the introduction of more demanding content are intended to raise standards and better prepare students for the next stages of their education or careers. This change also facilitates a more transparent differentiation among top grades, providing sixth forms, colleges, universities, and employers with a clearer understanding of student capabilities.
The introduction of the new 9-1 GCSE grade system marks a significant step towards elevating educational standards in England. By offering a more nuanced differentiation of student achievement, particularly at the higher end, it seeks to foster a culture of excellence and high achievement. As the system continues to bed in, the true impact of these changes on students, educators, and the broader educational landscape will become increasingly clear, hopefully reflecting the positive outcomes intended by this ambitious reform.
How to Apply to Sixth Forms?

To apply to sixth form (or post-16 education), you typically need to follow these steps:
📌 Research your options. Find out which sixth forms offer the courses you’re interested in. Look into their admission requirements and application deadlines.
📌 Prepare your application. This may include filling out an application form, writing a personal statement, providing reference letters, and submitting your previous exam results or grades.
📌 Submit your application. You can usually submit your application online or in person, depending on the institution’s preference.
📌 Attend an interview. Some sixth forms require applicants to attend an interview as part of the admission process. This is an opportunity for you to discuss your interest in the courses and answer any questions the admissions staff may have.
📌 Receive a decision. After reviewing your application, the sixth form (6th form) will notify you of its admission decision. If you’re accepted, you’ll be asked to confirm your enrollment and pay any required fees.
Note: The specific requirements and steps may vary depending on the institution and the country you’re applying to.
How to Know if Your Sixth Form (6th form) is Good?
When you are choosing a sixth form (6th form), it is important to look at the school’s reputation. You can find out about the reputation of different schools by:
📌 Reading reviews on websites such as Google Reviews.
📌 Asking people who have attended that sixth form (6th form) before (e.g., your friends).
📌 Looking at the information on their website and social media pages such as Facebook or Twitter – if they have any!
📌 Another thing to consider when looking at different schools’ quality is how well students perform in exams like GCSEs and A Levels (and sometimes BTECs). This shows how successful students have been in past years. This can give you an indication of what kind of results you might achieve.
📌 It is also important to consider the range of courses offered by the Sixth Form (6th form). Make sure that the courses you are interested in are available. Additionally, consider the extracurricular activities offered by the Sixth Form (6th form). These can be a great way to develop your skills and interests outside of the classroom.
What Happens If You Don’t Get Accepted into Sixth Form (6th form)?
If you don’t get accepted into sixth form (6th form), there are a number of things you can do to ensure that your academic career is not over.
📌 Take a gap year. If it seems as though your grades aren’t up to par, consider taking time off before reapplying in the future. Many students who reapply after taking time off tend to be more successful than those who don’t.
📌 Re-take GCSEs. You might be able to improve your chances by retaking certain subjects and getting higher grades this time around.
📌 Apply to other sixth forms. You could also consider applying for admission at another college or university within proximity. Just make sure that these institutions have similar entry requirements as yours so that they accept all of the courses you’ve passed over again.
To Sum Up
In order to apply for a place at a Sixth Form (6th form), there are some requirements that need to be met. These include having taken 5 GCSEs with grades of 4 or higher, including English and Mathematics, and possibly having higher grades in certain subjects in order to pursue certain A-Levels sixth form or vocational qualifications. Mock exam results may also be required as part of the application process. It is important to research a Sixth Form (6th form) prior to applying, in order to ensure it is a good fit for your academic goals. 🏫 If unsuccessful in your application for a place at a Sixth Form (6th form), there are still other options available.
If you need additional help with achieving the grades you need in your GCSEs, you can always find additional help. Expert tutors from Edumentors can help you ace your exams and even choose your A-level subjects.
Feel free to share this article with your fellow GCSE students. You never know how much even a little bit of information can help someone out!
Good luck!
FAQs:
What is the difference between sixth form and college?
Sixth form and colleges in the UK cater to students aged 16-18 but differ in focus. Sixth form often part of a secondary school, primarily offers A and AS-level courses for university preparation. Colleges offer a wider range of qualifications, including vocational training and specialized programs in fields like business or the arts, providing diverse pathways for further education or career entry.
Whats sixth form in the UK?
The sixth form is an educational institution designed exclusively for students who have finished their GCSEs. It provides A-Levels, BTECs, and various other qualifications, enabling young individuals to pursue further education in preparation for university or advanced learning.
Is sixth form the same as A-levels?
Sixth form and A-levels are connected, but they’re different. Sixth form is the last part of school in the UK for 16 to 18-year-olds. In these two years, students often work towards getting their A-levels. A-levels are exams students take at the end of sixth form in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland. So, think of sixth form as the time you’re in school, and A-levels as the big exams you take at the end of it.
Is GCSE a sixth form?
No, GCSE is not a sixth form. GCSEs are a set of exams taken by students in England, Wales, Northern Ireland, and some other Commonwealth countries, typically at the age of 15-16 years, at the end of compulsory schooling.
They cover a variety of subjects and are usually completed before students proceed to A-Levels, which are taken during sixth form at ages 16-18. Sixth form refers to the two years of school education (commonly known as Year 12 and Year 13 in England and Wales) that prepare students for A-Level exams, further education, and higher education.
What are the new GCSE grades?
- England now uses 9–1 grades (9 highest, 1 lowest), replacing A–G*.
- Rough equivalents: 7 ≈ A, 4 ≈ C (standard pass), 5 = strong pass.
- 9 is rarer than A*.
Boundaries vary each year to keep standards fair.
What age is sixth form in the UK?
In the UK, sixth form refers to the final two years of secondary education, which are usually attended by students aged 16 to 18. This stage covers Years 12 and 13, where students typically study for A-Levels, BTEC qualifications, or other equivalent qualifications.
Is sixth form the same as a level?
Sixth form and A Levels are related but not the same. Sixth form refers to the two years of education (Years 12 and 13) that students undergo typically between the ages of 16 and 18 in the UK. During sixth form, students can choose to study for various qualifications, of which A Levels are the most common. However, they might also choose other pathways like BTEC diplomas or the International Baccalaureate. So, while A Levels are a common choice taken during sixth form, they are just one of several options available to students during this period of education.
Is sixth form after GCSE?
Yes, sixth form is the stage of education that follows GCSEs in the UK. Students typically enter sixth form at the age of 16, after completing their GCSE examinations. Sixth form comprises two years of study, Year 12 and Year 13 during which students usually study for A-levels, BTEC qualifications, or other equivalent courses. This stage is crucial for preparing students for higher education, apprenticeships, or employment.








