Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis (A-Level Biology): A Complete Guide
Photosynthesis is how plants transform light energy into chemical energy, fueling their growth and survival. This process is essential in biology, especially when studying the limiting factors of photosynthesis (A-Level Biology). These factors reveal how efficiently plants perform photosynthesis under different environmental conditions.
In A-Level Biology, understanding the factors that affect photosynthesis is crucial for exploring how plants interact with their environment. For photosynthesis, these factors include light intensity, carbon dioxide levels, and temperature, all of which play a critical role in energy production and plant health. A limiting factor, by definition, is any condition that restricts the rate of a biological process when in short supply. Knowing the limiting factor definition in biology helps explain why photosynthesis slows or stops under specific conditions, offering valuable insights into plant behavior.
By exploring this topic, you’ll discover how plants harness light energy to sustain life on Earth. It also highlights why studying photosynthesis is essential for understanding ecosystems and improving crop management.
What is Photosynthesis?
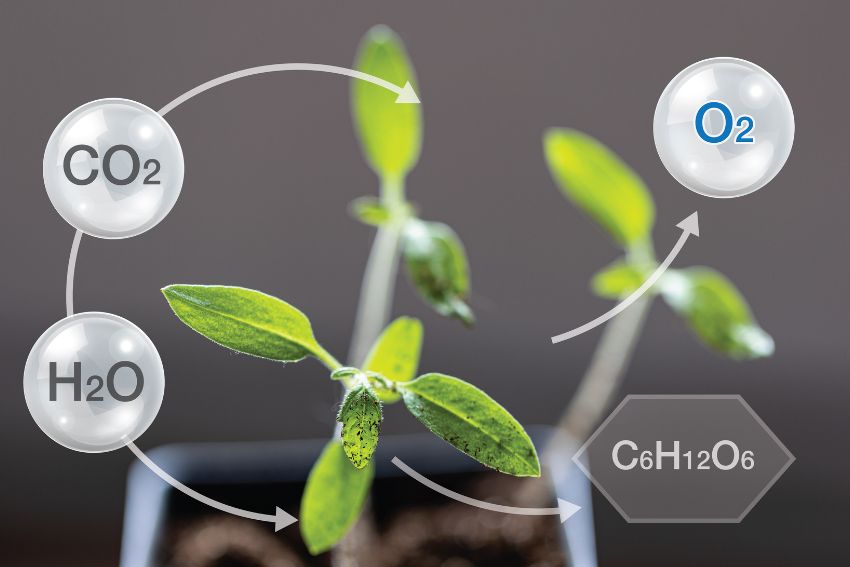
Photosynthesis is the process where plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy in the form of glucose. This vital process occurs in the chloroplasts, where chlorophyll, a green pigment, captures light energy to power the reaction. Among the inputs, carbon dioxide is the key gas needed by plants for photosynthesis, along with water.
In A-level Biology, understanding this process is fundamental for analyzing the factors affecting photosynthesis. Light intensity, water availability, and carbon dioxide levels are not only essential for photosynthesis but also directly impact how efficiently plants produce energy.
The chemical equation for photosynthesis demonstrates this transformation:
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2Here, six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water are converted into glucose and oxygen, fueled by light energy.
By exploring this process, you’ll gain insights into how plants sustain themselves and why environmental conditions play a critical role in photosynthesis.
3 Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
| Limiting Factor | Description | Impact on Photosynthesis |
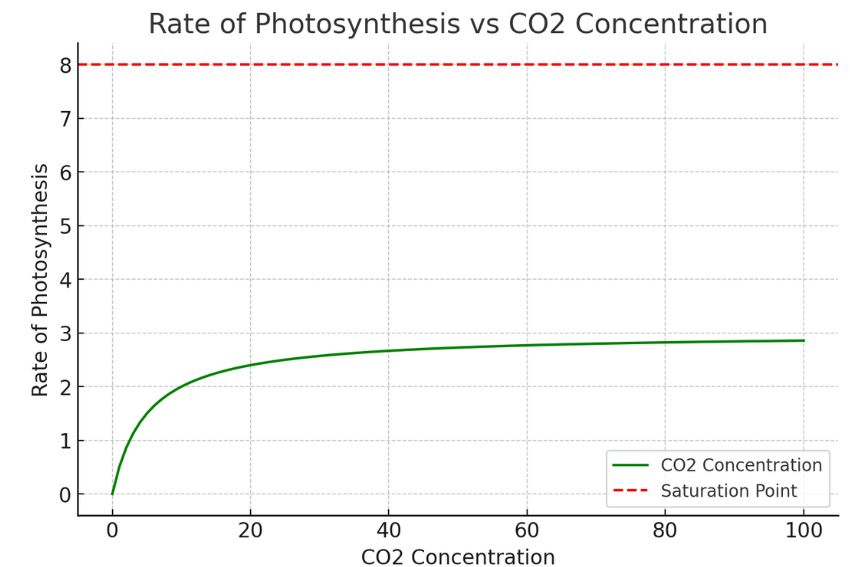
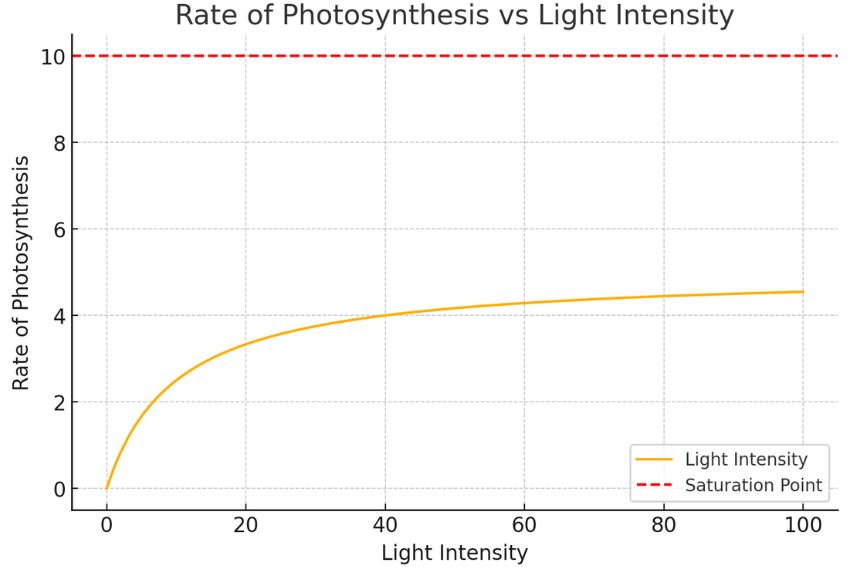
| Light Intensity | Light provides energy for photosynthesis; insufficient light reduces the rate. | Rate increases with light intensity until it reaches a saturation point. |
| Carbon Dioxide Concentration | CO₂ is a key reactant; low levels limit the Calvin Cycle. | Optimum temperature maximizes enzyme activity, but extreme temperatures denature enzymes. |
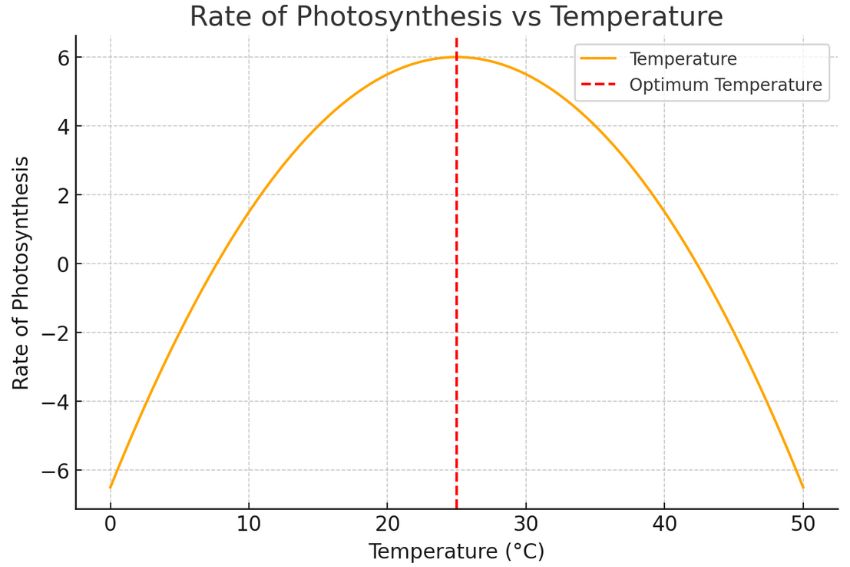
| Temperature | Enzymes involved in photosynthesis are temperature-sensitive; too high or low temperatures affect efficiency. | Optimum temperature maximizes enzyme activity, but extreme temperatures denature enzymes. |
Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
While photosynthesis is vital for plants, its efficiency depends on specific environmental conditions. These conditions, known as limiting factors, play a key role in determining how effectively plants can produce energy. In A-level Biology, understanding the limiting factors of photosynthesis is essential for analyzing how external factors impact this critical process.
A limiting factor, by definition in biology, is any condition that restricts the rate of a biological process when it is in short supply. For photosynthesis, this means light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature are the primary elements that can either enhance or slow down the process.
The relationship between these factors and the rate of photosynthesis can often be visualized through graphs. These rate of photosynthesis graphs help demonstrate how changes in each factor directly impact the process. Let’s explore each of these limiting factors in more detail to understand their significance.
Additional Factors that Affect Photosynthesis
In addition to light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature, other elements can influence the efficiency of photosynthesis. These factors affecting photosynthesis play a significant role in how well plants convert light energy into chemical energy. While not always classified as primary limiting factors of photosynthesis, their impact cannot be overlooked.
Water Availability
Water is an essential component of the photosynthetic process, as it provides the hydrogen which is necessary to form glucose. When water is scarce, plants close their stomata to prevent water loss. However, this also reduces the intake of carbon dioxide, slowing photosynthesis. Therefore, water scarcity indirectly becomes one of the factors affecting photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll Concentration
Chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants, is crucial for capturing light energy. A reduction in chlorophyll levels-due to nutrient deficiencies or environmental stress-can significantly decrease photosynthesis efficiency. Without enough chlorophyll, plants struggle to absorb sufficient light, directly limiting the process.
Thus, understanding these additional factors helps answer the question, “What are the limiting factors of photosynthesis?” While light, carbon dioxide, and temperature are the primary factors, water and chlorophyll levels can also greatly influence the rate of photosynthesis.
The Calvin Cycle in A-Level Biology
While light is crucial for photosynthesis, the Calvin Cycle represents the light-independent stage, where plants convert carbon dioxide into glucose. In A-level Biology, understanding the Calvin Cycle is essential for grasping how energy captured during the light-dependent stage is utilized to produce carbohydrates. This process takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts and is a key aspect of the factors affecting photosynthesis.
Stages of the Calvin Cycle
- Carbon Fixation: Carbon dioxide combines with ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), facilitated by the enzyme RuBisCO, to form two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA).
- Reduction Phase: ATP and NADPH, generated during the light-dependent reactions, convert 3-PGA into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), a sugar molecule.
- Carbohydrate Formation: Some G3P molecules are used to synthesize glucose and other carbohydrates.
- Regeneration of RuBP: The remaining G3P molecules regenerate RuBP, allowing the cycle to continue.
How Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis Influence The Calvin Cycle
The Calvin Cycle is heavily influenced by the limiting factors of photosynthesis. For instance:
- Carbon Dioxide: Insufficient CO₂ levels reduce carbon fixation, slowing the entire cycle.
- Light Intensity: Although the Calvin Cycle is light-independent, it relies on ATP and NADPH, which are products of the light-dependent reactions. Low light limits these energy carriers, indirectly affecting the cycle.
- Temperature: The enzymes involved in the Calvin Cycle, such as RuBisCO, are sensitive to temperature changes. Extreme temperatures can reduce their efficiency.
By exploring the Calvin Cycle in A-level Biology, students gain a deeper understanding of how plants convert energy into sugars and how environmental conditions impact this process.
Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis: Practical Applications
Understanding the limiting factors of photosynthesis (A-Level Biology) has practical applications, especially in agriculture. Farmers can manipulate environmental conditions to optimize the rate of photosynthesis in crops, leading to higher yields and better productivity. By adjusting factors such as light intensity, carbon dioxide levels, and temperature, farmers can ensure that these elements never become limiting.
For example, in controlled environments like greenhouses, artificial lighting is used to extend daylight hours, ensuring plants receive enough light for photosynthesis. Similarly, carbon dioxide enrichment systems increase CO₂ concentrations, accelerating the process. Temperature control systems maintain optimal conditions, preventing enzymes in the Calvin Cycle from denaturing or becoming inactive.
The role of the Calvin Cycle in photosynthesis is especially significant in agricultural practices, as it converts the energy and carbon dioxide into glucose needed for plant growth. By understanding how limiting factors affect the rate of photosynthesis, farmers can take targeted measures to boost plant health and crop yields. This knowledge is not only vital for productivity but also for efficient resource management in modern farming.
Conclusion
Understanding the limiting factors of photosynthesis (A-Level Biology) is crucial for both academic success and practical applications. Throughout this blog, we explored the key factors affecting photosynthesis, such as light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature, as well as their impact on the Calvin Cycle in plants. We also discussed how these factors can be managed in controlled environments to optimize productivity in agriculture.
For students studying A-Level Biology, mastering these concepts is essential to understanding how plants interact with their environment and sustain life on Earth. This knowledge is not only valuable for exams but also for practical applications, such as improving crop yields and managing resources effectively.
If you need extra help understanding these topics, consider reaching out to online A-Level Biology tutors. They can provide personalized guidance and make challenging concepts easier to grasp. By deepening your understanding of photosynthesis, you’ll gain insights into one of biology’s most fascinating processes and its vital role in supporting life.
FAQs
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen. It’s essential for plant survival and energy transfer within ecosystems.
What are the limiting factors of photosynthesis?
The primary limiting factors of photosynthesis include light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature. Each of these can directly affect how efficiently photosynthesis occurs.
What is a limiting factor in photosynthesis?
A factor that prevents any increase in photosynthesis is called a limiting factor. It restricts the rate of photosynthesis when it is in short supply
What are the 3 limiting factors of photosynthesis?
The three main limiting factors of photosynthesis are:
Temperature: Affects enzyme activity involved in photosynthesis.
Light Intensity: Determines the energy available for the process.
Carbon Dioxide Concentration: A crucial input for the Calvin Cycle.
How do limiting factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Limiting factors reduce the rate of photosynthesis by restricting one or more essential conditions. For instance, low light intensity limits energy absorption, while low CO₂ reduces glucose production.
What gas is needed by plants for photosynthesis?
Plants need carbon dioxide (CO₂) for photosynthesis. This gas is a key input in the process and is used during the Calvin Cycle to produce glucose.
What is the role of the Calvin Cycle in photosynthesis?
The Calvin Cycle, also known as the light-independent stage, converts carbon dioxide into glucose using ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions. It plays a vital role in producing energy-rich carbohydrates for plant growth.