Exothermic Reaction Profile – A Simple Guide For GCSE Chemistry
Understanding exothermic reaction profile is important part of GCSE Chemistry. They show how energy changes during chemical reactions, helping you understand why some reactions release heat.
Energy changes play a key role in many chemical processes, from everyday activities like using hand warmers to industrial applications such as fuel combustion. By Learning this topic, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how reactions work and their practical implications.
In this blog, we’ll explore exothermic reaction profile in detail. You’ll learn what they are, how they differ from endothermic profiles, and how to interpret their diagrams effectively. Additionally, we’ll cover examples, key features, and tips to tackle related exam questions better. Let’s explore how energy changes shape the reactions around us!
What is an Exothermic Reaction?
An exothermic reaction is a type of chemical reaction that releases energy into its surroundings, often as heat. As a result, these reactions usually cause an increase in temperature, which makes them easy to notice in everyday life. Furthermore, GCSE Chemistry is a subject focused on understanding chemical reactions, materials, and the properties of matter. Therefore, topics like exothermic reactions play a crucial role in the curriculum.
Real-World Examples:
Combustion: Burning fuels like wood or gas releases heat, making this a common exothermic reaction.
Hand Warmers: These use chemical reactions to produce heat, keeping you warm in cold weather.
Neutralisation Reactions: Mixing an acid and a base generates heat, a clear sign of an exothermic process.

Why Do Exothermic Reactions Release Energy?
Chemical reactions break old bonds and form new ones. Breaking bonds uses energy, while forming bonds releases it. In exothermic reactions, bond formation releases more energy than bond breaking consumes. This difference causes a net energy release, which we experience as heat.
By understanding this balance, you can better explain why exothermic reactions are so important in both nature and industry.
What is a Reaction Profile?
A reaction profile shows how energy changes during a chemical reaction. The diagram highlights the energy difference between the reactants and products and helps you determine whether energy is absorbed or released.
Understanding the Axes : The vertical axis represents energy levels and the horizontal axis represents the progress of the reaction from start to finish.
Reaction Profile diagram Explained
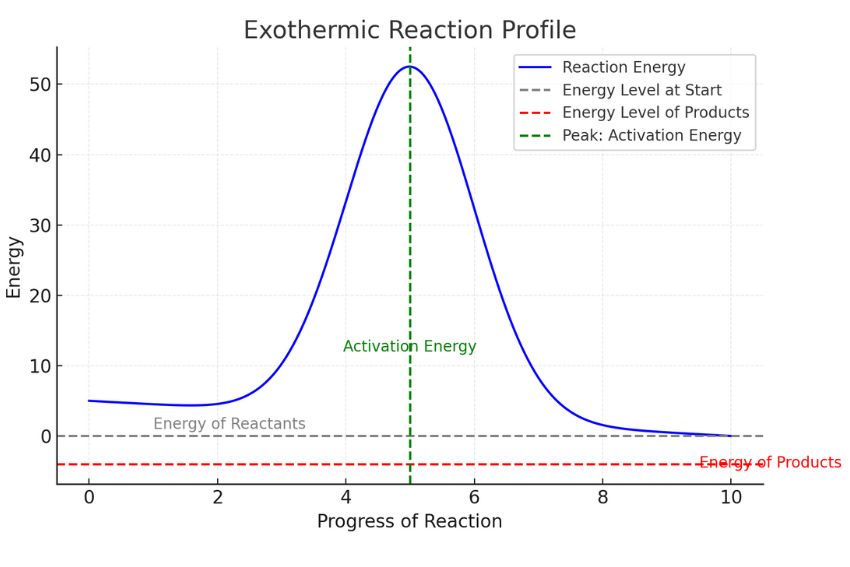
In a reaction profile, you’ll notice a curve or hump in the graph. This hump represents the energy required to start the reaction, known as activation energy. For an exothermic reaction, the energy level of the products is lower than that of the reactants. Shows that energy has been released into the surroundings during the reaction.
By using reaction profiles, you can easily identify whether a reaction is exothermic or endothermic, making them a key tool in GCSE Chemistry.
Features of an Exothermic Reaction Profile
An exothermic reaction profile highlights key energy changes during a chemical reaction. Let’s break it down:
Key Components of Exothermic Reaction Profile
Energy Released to Surroundings
In exothermic reactions, energy is released, often as heat. This is why the products feel warm.
Downward Slope from Reactants to Products
The profile shows that the energy level of the products is lower than the reactants. This decrease represents the energy released.
Activation Energy (Hump on the Graph)
Every reaction needs some energy to start. This energy is shown as a hump on the graph. In fact, the higher the hump, the more energy is needed to begin.
Visualising the Profile
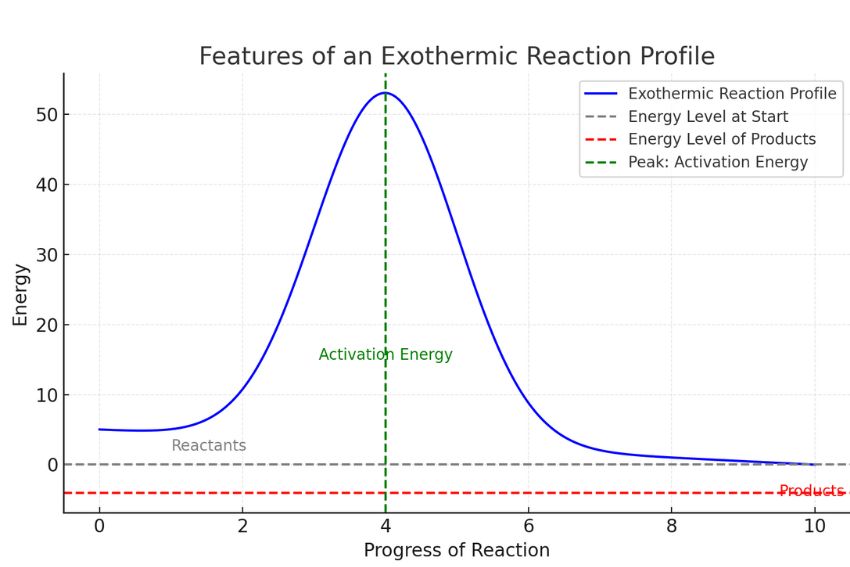
Imagine a graph like this :
- The y-axis represents energy levels.
- The x-axis represents the progress of the reaction.
At the start, the energy is high (reactants). It peaks at the hump (activation energy) and then drops significantly to a lower energy level (products).
This downward slope makes a reaction exothermic-it demonstrates how energy releases into the surroundings. Including diagrams like the one above helps you understand these components visually, which is especially useful for GCSE Chemistry exams.
Comparing Exothermic and Endothermic Reaction Profiles
Knowing the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions is a must for learning energy changes in GCSE Chemistry. Reaction profiles help illustrate these differences visually.
Exothermic Reaction Profile
Energy Decreases: The products have less energy than the reactants.
Energy Released: Heat is transferred to the surroundings, making the reaction warm or hot.
Example: Combustion reactions, such as burning fuels
Endothermic Reaction Profiles
Energy Increases: The products have more energy than the reactants.
Energy Absorbed: Heat is taken in from the surroundings, causing the reaction to feel cold.
Example: Melting ice or photosynthesis.
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Exothermic | Endothermic |
| Energy Change | Energy decreases | Energy increases |
| Products Energy Level | Lower than reactants | Higher than reactants |
| Heat Transfer | Released to surroundings | Absorbed from surroundings |
Reaction profiles clearly show these contrasts. In exothermic reactions, the graph slopes downward because the reaction releases energy, while in endothermic reactions, it slopes upward as the reaction absorbs energy.
Why is Activation Energy Important?
What is Activation Energy? activation energy is the minimum amount of energy needed for a chemical reaction to begin. Hence, It acts as a barrier that reactants must overcome to form products. Without enough energy, the reaction won’t start.
For example, when lighting a match, the friction provides activation energy, allowing the chemicals in the match to react and produce heat and light.
The Role of Catalysts in Lowering Activation Energy
Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required. As a result, reactions occur more quickly and efficiently. In addition, in reaction profiles, the graph shows catalysts as a smaller hump, indicating their effect on the reaction. Here’s how they work:
Without a Catalyst: The energy required to start the reaction is high, making it slower or harder to begin.
With a Catalyst: The activation energy is reduced, making it easier for reactants to transform into products.
This concept is a key part of the GCSE Chemistry syllabus as it links to reaction rates and energy changes. Learning how catalysts affect activation energy helps explain their importance in both biological processes, like enzyme activity, and industrial applications, like manufacturing.
Applications of Exothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions are not just theoretical; in fact, they have practical uses in everyday life and industry. For instance, by linking these reactions to real-world applications, you can gain a deeper understanding of their significance. Moreover, this connection helps demonstrate how exams test exothermic reactions, reinforcing both their relevance and the methods used to assess them
Everyday Examples:
Combustion: Burning fuels like wood, coal, or gas releases heat and light. This powers heating systems, cooking, and transportation.
Respiration: Inside cells, glucose reacts with oxygen to release energy, water, and carbon dioxide. This process keeps living organisms alive.
Neutralisation Reactions: When acids and bases mix, they release energy as heat, which can be felt during experiments.
Industrial Applications
Fuel Burning: Many industries rely on combustion to generate heat and energy for machinery and power plants.
Heat Packs: These packs use exothermic reactions to release heat quickly, offering practical solutions for sports injuries or warming hands in cold weather.
How Understanding Exothermic Reaction Profile Helps in GCSE Chemistry Exams
- Reaction profiles show how energy transfers in these processes, helping you visualise the concept more clearly.
- You’ll be able to answer questions about energy changes, reaction diagrams, and the practical uses of exothermic reactions.
- Recognising these real-world links can make the topic easier to understand and memorise, which is especially useful for exam preparation.
Mastering exothermic reactions and their profiles, you can connect chemistry theory to everyday and industrial processes, building both understanding and confidence for your GCSE exams.
GCSE Chemistry Exam Questions on Exothermic Reaction Profile
Exothermic reaction profile often appear in GCSE Chemistry exams, testing your understanding of energy changes and reaction diagrams. For instance, here are some common types of questions you might encounter, along with tips to answer them effectively.
Typical Exam-Style Questions
- Interpret a Reaction Profile Diagram
You may be asked to describe a reaction profile diagram, highlighting key features such as the initial energy of the reactants, the peak showing activation energy, and the final energy of the products. For exothermic reactions, focus on the downward slope, which indicates energy release. - Explain Energy Changes in an Exothermic Reaction
This question typically requires you to explain that more energy is released when bonds form than is used to break the original bonds. Include terms like “net energy release” and mention how this energy is transferred to the surroundings, often as heat. - Identify Activation Energy on a Graph
You might be given a reaction profile and asked to point out the activation energy. Look for the peak of the curve between the reactants and the highest energy point on the graph. Clearly describe this as the energy needed to start the reaction.
Tips for Answering Effectively
- Use Clear Terminology: Always use key terms like “reactants,” “products,” “activation energy,” and “energy release.” These demonstrate a strong understanding of the topic.
- Refer to the Diagram: When answering, refer directly to the diagram provided in the question to ensure clarity. For example, mention the slope or peak when discussing energy changes.
- Practise Drawing Diagrams: Practise drawing exothermic reaction profile with proper labelling. By doing this, you will not only improve your understanding but also feel more confident if asked to reproduce or annotate one in an exam.
- Keep Explanations Simple: Write concise answers that clearly describe the energy flow and key components without unnecessary complexity.
If you preactise these question types and use the tips , you’ll be prepared to tackle any exam questions related to exothermic reaction profile.

Study Tips for Mastering Exothermic Reaction Profile In GCSE Chemistry
To get better in exothermic reaction profile, use visual aids, practise regularly, and stay actively involved. Here are some helpful tips to get better at this topic:
Use Clear Diagrams
Visual aids are very helpful when studying exothermic reaction profile. Look at diagrams with labels for key parts like reactants, products, activation energy, and energy release. Diagrams make it easier to understand and remember these concepts.
Practise Drawing and Reading Graphs
Draw reaction profiles often, including important details like the downward slope and activation energy hump. Also, practise reading graphs to explain energy changes accurately.
Explain Concepts Out Loud
Test yourself by explaining the ideas out loud, either to yourself or a friend. For example, talk about how energy changes in an exothermic reaction and how the graph shows it. This helps reinforce what you’ve learned.
Use Online Tools and Simulations
Interactive websites like BBC Bitesize or PhET simulations make learning fun. They show energy changes in action, helping you better understand and enjoy the topic.
If you combine these study methods, you’ll build a strong understanding of exothermic reaction profile, boosting both your confidence and your exam performance.
Conclusion
Exothermic reaction profile is important part of GCSE Chemistry. They clearly demonstrate how reactants release energy as they change into products. As a result, this makes it easier to understand energy changes in reactions. Additionally, learning about activation energy and energy transfer will further help you understand this topic better.
To master this topic, practise regularly. Draw reaction profiles, label important parts like activation energy and energy released, and explain them in simple words. This will boost your confidence and help you do better in exams.
If you need extra help, consider online tutoring in GCSE Chemistry. A tutor can guide you through reaction profiles, explain tricky concepts, and help you go through exam questions. Personalised support can make a huge difference in how well you understand these ideas. Keep practising and stay curious. You’ve got everything you need to succeed-keep going!
FAQ’s
What is the profile of an exothermic reaction?
An exothermic reaction profile shows the energy change during a reaction. It starts with reactants at a higher energy level and ends with products at a lower energy level. The difference in energy is released as heat or light. The curve usually dips, highlighting the energy drop and release.
How do you tell if a reaction profile is endothermic or exothermic?
You can tell by looking at the energy levels in the reaction profile:
In an exothermic reaction, the products are at a lower energy level than the reactants, releasing energy.
In an endothermic reaction, the products are at a higher energy level, as energy is absorbed during the reaction.
A downward curve indicates exothermic, while an upward curve shows endothermic.
How to draw a reaction profile for an exothermic reaction?
To draw an exothermic reaction profile:
- Start by drawing a y-axis for energy and an x-axis for the reaction pathway.
- Plot the reactants at a higher energy level.
- Draw a curve that rises slightly (representing the activation energy) before falling to a lower energy level for the products.
- Label the activation energy and show the energy released by drawing a downward arrow.
What are 5 examples of exothermic reactions?
Here are five common exothermic reactions:
Freezing: Liquid water freezing into ice releases heat energy.
Combustion: Burning fuels like wood, coal, or gasoline.
Neutralisation: Mixing an acid with an alkali (e.g., HCl + NaOH).
Respiration: The process cells use to release energy from glucose.
Condensation: Water vapour turning into liquid releases heat.
Is GCSE chemistry hard?
GCSE Chemistry can be challenging, but it depends on how you approach the subject. Some students find it tricky due to the mix of theory, equations, and practical experiments, while others enjoy the logical problem-solving aspects.