Key Stages and Ages: School Years Made Simple For Parents
The UK education system structures Key Stages to guide a child’s learning journey from early years to secondary school. Each stage corresponds to specific school years and age groups, which makes it easier to track progress and key achievements. By understanding these Key Stages, you can better support your child’s learning and overall growth.
In this blog, we’ll provide a clear and simple breakdown of KS1, KS2, KS3, KS4, and KS5, focusing on the ages, school years, and key features of each stage. Whether you’re new to the UK education system or just looking to understand it better, this guide is here to help. Let’s explore each stage and learn how to make the most of these important years in your child’s education.
- Key Stages: What Happens at Each Stage?
- Why Do Ages Matter in the Key Stages?
- Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS): Objectives and Learning Approaches for Ages 3-5
- Key Stage 1: Building the Foundation
- Key Stage 2: Expanding Knowledge
- Key Stage 3: Transition to Secondary Education
- Key Stage 4: Preparing for GCSEs
- Key Stage 5: Pathways to Higher Education and Careers
- Conclusion
Key Stages: What Happens at Each Stage?
Before we dive deeper into the KS Ages , let’s briefly overview key stages first. As you know, the national curriculum divides into key stages, matching students’ age and learning needs.
Key Stage 1 (KS1)
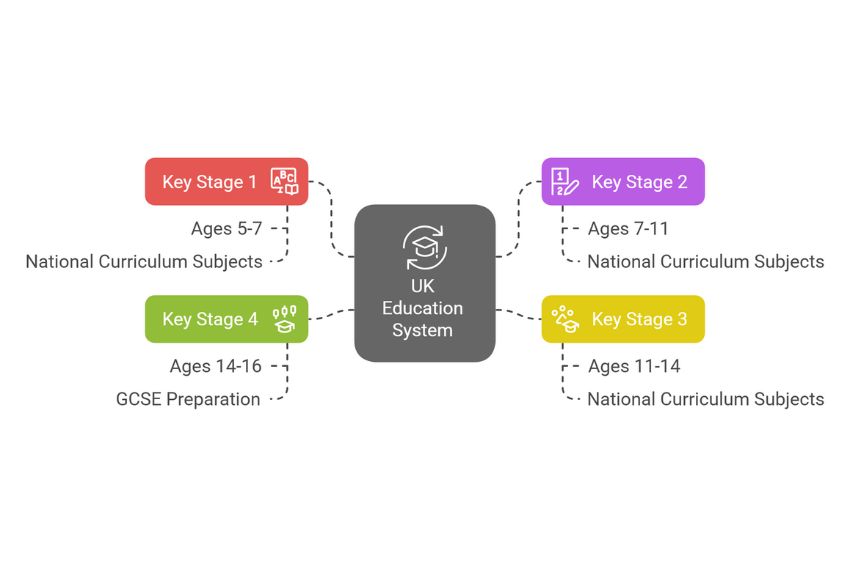
What is Key Stage 1? KS1 is for children aged 5 to 7 in Years 1 and 2. It focuses on building basic skills in reading, writing, and maths. At the end of Year 2, children take SATs, which help teachers understand how they’re progressing and where extra support might be needed.
Key Stage 2 (KS2)
Key Stage 2 covers Years 3 to 6 for children aged 7 to 11. They learn more subjects, like science, geography, and history, while improving their core skills. In Year 6, children take KS2 SATs, which prepare them for secondary school.
Key Stage 3 (KS3)
Key Stage 3 introduces children to secondary school, covering Years 7 to 9 for ages 11 to 14. Students study a wider range of subjects, including languages, technology, and personal development, while developing important skills like critical thinking and problem-solving.
Key Stage 4 (KS4)
KS4 is for students aged 14 to 16, in Years 10 and 11. At this stage, the focus shifts to preparing for GCSE exams, which they take at the end of Year 11. During this time, students study core subjects like English, maths, and science. Additionally, they choose optional subjects that align with their interests and future career goals.
Why Do Ages Matter in the Key Stages?
Understanding how ages align with the Key Stages is important for parents because it provides clarity on their child’s educational journey. For instance, each Key Stage matches specific age ranges, ensuring that children progress at a pace suited to their development. Moreover, this age-based system helps schools create lessons and activities that match a child’s needs, supporting their learning and growth.
Knowing these age ranges helps parents set realistic expectations for their child’s academic progress. It also allows you to understand what’s suitable for your child’s age, making it easier to support them. Whether it’s helping with homework or discussing topics they’re learning in school, understanding their Key Stage makes a big difference.
Now, let’s explore a detailed breakdown of each Key Stage and its matching age group. This will give you a clear picture of what to expect at each stage of your child’s education.
| Key Stage | School Years | Age Range |
|---|---|---|
| Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS) | Nursery and Reception | 3–5 years old |
| Key Stage 1 (KS1) | Years 1–2 | 5–7 years old |
| Key Stage 2 (KS2) | Years 3–6 | 7–11 years old |
| Key Stage 3 (KS3) | Years 7–9 | 11–14 years old |
| Key Stage 4 (KS4) | Years 10–11 | 14–16 years old |
| Key Stage 5 (KS5) | Years 12–13 | 16–18 years old |
Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS): Objectives and Learning Approaches for Ages 3-5
The Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS) is a crucial part of the UK education system, catering to children aged 3 to 5. This stage covers Nursery and Reception years, helping young learners develop skills and attitudes essential for their future school years. By focusing on both academic and personal growth, EYFS sets the foundation for a smooth transition into Key Stage 1.
EYFS aims to nurture children’s overall development through play-based and hands-on learning experiences. It provides an environment where children can explore, create, and engage with others while gradually acquiring the skills needed for formal education.
Learning Approaches for Ages 3-5
The EYFS framework focuses on play-based learning, thereby enabling children to learn in a natural and engaging way. Furthermore, activities are designed to align with the child’s developmental stage and foster curiosity, creativity, and collaboration.
- Play and Exploration: Children are encouraged to explore their interests through unstructured and guided play, which helps them develop problem-solving skills and social abilities.
- Hands-On Activities: Practical tasks, such as assembling puzzles or creating crafts, enhance fine motor skills and spatial awareness.
- Interactive Storytelling: Reading stories aloud and singing songs help develop comprehension, listening, and language skills.
- Outdoor Learning: Activities in outdoor environments, such as gardening or group games, promote physical health and awareness of nature.
- Focused Group Tasks: Short, interactive lessons introduce foundational concepts like the alphabet and numbers in a fun and accessible way.
Importance of EYFS for Future School Years
The EYFS stage plays a vital role in preparing children for the structured learning environment of Key Stage 1. Moreover, by promoting confidence, curiosity, and foundational skills, EYFS ensures children are well-prepared for the academic and social challenges of primary school. Additionally, it sets the stage for lifelong learning by fostering resilience, adaptability, and a love for discovery.
Key Stage 1: Building the Foundation
Key Stage 1 (KS1) is a vital phase in the UK education system, designed for children aged 5 to 7, covering Years 1 and 2 of primary school. This stage builds upon the Early Years Foundation Stage, introducing children to a more structured learning environment while fostering critical skills and knowledge. KS1 lays the groundwork for future academic success by focusing on fundamental subjects and essential learning habits.
Curriculum Focus for KS1 Ages 5-7
The KS1 curriculum is designed to provide a broad and balanced education. It includes core and foundation subjects that encourage both academic and personal growth.
Assessments in Key Stage 1
Assessments in KS1 are designed to measure children’s progress and identify areas where additional support may be needed. These evaluations ensure that each child is on track with their learning objectives.

Importance of Key Stage 1 for Future Education
Key Stage 1 establishes a strong foundation for the educational journey ahead. Moreover, by focusing on essential literacy and numeracy skills, as well as fostering creativity and curiosity, KS1 equips children with the tools they need to succeed in Key Stage 2 and beyond. Therefore, it plays a crucial role in setting the stage for future academic and personal growth. The balance between structured learning and creative exploration ensures that children develop academically, socially, and emotionally during these formative years.
Key Stage 2: Expanding Knowledge
Key Stage 2 (KS2) is for children aged 7 to 11 and includes Years 3 to 6. This stage builds on the basics learned in Key Stage 1. It introduces more subjects and deeper learning. KS2 helps children get ready for secondary school by teaching them to think independently and take on more responsibility.
Subject Areas for KS2 Ages 7-11
In KS2, children study a wide range of subjects. These include English, Maths, and Science, as well as History, Geography, Art, and Music. Physical Education helps with fitness, while Computing introduces technology skills. Children may also learn a foreign language. These subjects encourage curiosity and help children grow academically.
Preparation for Secondary Education
KS2 prepares children for secondary school. It teaches important skills like reading, writing, and problem-solving. Children also learn to work with others and manage their time. By the end of KS2, they are more confident and ready to handle the demands of Key Stage 3.
Importance of Key Stage 2 for the Future
Key Stage 2 is an important bridge between primary and secondary school. Moreover, it gives children the knowledge and confidence they need to succeed in the next stage of learning. In addition to academic skills, it also builds resilience and independence, both of which are essential for their future success in school and beyond.
Key Stage 3: Transition to Secondary Education
Key Stage 3 (KS3) is for students aged 11 to 14 and covers Years 7 to 9. It marks the start of secondary school and introduces a wider, more structured curriculum. This stage helps students move from primary school to more advanced learning.
Academic Development for KS3 Ages 11-14
At KS3, students build on what they learned in primary school. Core subjects like English, Maths, and Science are still important. Students also study a range of other subjects, including History, Geography, Art, Music, and Physical Education.
New subjects, such as Computing and Modern Foreign Languages, are added. This variety gives students a chance to learn about different fields. It also helps them develop skills like problem-solving and critical thinking.

Subject Specialisation
In KS3, teachers who specialise in their subjects teach students. For example, they often divide Science into Biology, Chemistry, and Physics. This approach gives students a deeper understanding of each subject and helps them prepare for GCSE choices at the end of KS3.
Specialisation lets students explore what they enjoy and are good at. It helps them decide what subjects they may want to study more in the future.
Importance of Key Stage 3
KS3 is about more than just learning subjects. It helps students grow as individuals. They learn skills like working independently, being part of a team, and staying resilient. These years are important for adjusting to the demands of secondary school.
By the end of KS3, students should know their strengths and interests. This understanding helps them make good choices about what to study next. KS3 builds a strong base for success in later years, both academically and personally.
Key Stage 4: Preparing for GCSEs
Key Stage 4 (KS4) is a key part of the UK education system for students aged 14 to 16. It includes Years 10 and 11. During this time, students prepare for their General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) exams. These exams play an important role in deciding their future education and career paths. KS4 focuses on building knowledge, developing key skills, and getting ready for further studies.
Examination Structure for KS4 Ages 14-16
The GCSE exams are the main focus of Key Stage 4. These exams assess students’ knowledge and skills in different subjects. Most students take their GCSE exams at the end of Year 11.
GCSE grades are based on a mix of final exams and, in some cases, coursework or practical work. This system ensures students are judged on both their theoretical understanding and practical abilities.
Subject Choices for Ages 14-16
Students study core subjects like English, Maths, and Science. In addition, they choose optional subjects that match their interests and goals. Options can include:
- Humanities, such as History or Geography.
- Creative subjects, like Art or Music.
- Practical courses, such as Business Studies or Computer Science.
- Languages, including French, Spanish, or German.
Some schools also offer vocational courses like BTECs or Cambridge Nationals. These courses are practical and prepare students for specific careers.
Preparing for Post-16 Education
Key Stage 4 helps students get ready for the next step in their education. The subjects they choose and the skills they gain at this stage often shape their future options. After GCSEs, students may go on to study A-Levels, vocational courses, or take up apprenticeships.
Many students at this stage work towards Level 1 qualifications, especially if they are not yet achieving a standard pass in GCSEs. These include GCSEs at grades 1–3, functional skills, or foundation-level vocational courses. Level 1 qualifications provide a solid base for progressing to Level 2 or post-16 education pathways.
Importance of KS4 for Ages 14–16
Key Stage 4 is an important time for students because it marks a significant transition in their education. During this stage, they move from general learning to a more focused study, which allows them to delve deeper into subjects they enjoy. As a result, this stage helps students find their strengths while also developing confidence in their abilities. Moreover, by the end of KS4, they complete their education ready for the next stage and carry the skills and knowledge to achieve their future goals.
Key Stage 5: Pathways to Higher Education and Careers
Key Stage 5 is the final stage of secondary education in the UK, focusing on students aged 16 to 18. This stage is commonly referred to as Sixth Form and serves as a bridge between compulsory education and higher education or career opportunities. KS5 allows students to specialise in subjects of their choice, providing advanced knowledge and skills needed for their future aspirations.

Advanced Studies for KS5 Ages 16–18
In KS5, students transition to advanced courses, which are significantly harder and require more independent work. Generally, most students choose pathways such as A-Levels, BTECs, or other vocational courses. For instance, A-Levels primarily focus on three or four academic subjects, providing in-depth knowledge for further education. On the other hand, BTECs and vocational courses emphasise practical skills, preparing students for careers in fields such as business, healthcare, or engineering.
The choice of course depends on what the student wants to do in the future. A-Levels are best for students planning to go to university. Vocational courses are better for students who want hands-on learning or want to start work soon.
Qualifications Offered in Key Stage 5
A-Levels are assessed through exams at the end of two years. Students need to show deep understanding and problem-solving skills. Vocational courses mix practical work with coursework, which suits students who prefer learning by doing. Some schools and colleges allow students to take both A-Levels and vocational courses.
KS5 qualifications can lead to:
- Level 5 Qualification: e.g. foundation degrees, HNDs, and diplomas of higher education
- Level 7 Qualification: e.g. master’s degrees and postgraduate diplomas
- Level 8 Qualification: e.g. doctoral degrees such as PhDs
Preparation for Higher Education and Careers
KS5 prepares students for life after school. Those going to university earn UCAS points from their A-Level grades. Others gain skills and experience for jobs or apprenticeships.
This stage also helps students build key skills, such as managing time, working on their own, and solving problems. Schools provide career advice to help students decide on their next steps.
Importance of KS5 for Ages 16–18
Key Stage 5 is a time for students to focus on their future. They study subjects that match their goals and interests. This helps them prepare for higher education or a career. KS5 gives students the confidence and knowledge they need to succeed. It is not just about exams – it is about getting ready for life.
Conclusion
The UK education system is built around clear key stages that guide children from early years to adulthood. Each stage is designed to match the needs of specific age groups, supporting both academic and personal growth.
The Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS) introduces play-based learning for ages 3-5. Next, Key Stage 1 focuses on building basic skills in reading, writing, and maths for children aged 5-7. Then, Key Stage 2 builds on these abilities for ages 7-11, preparing students for secondary school. Following this, in Key Stage 3, students aged 11-14 begin exploring more specialised subjects to broaden their knowledge. After that, Key Stage 4, for ages 14-16, focuses on preparing students for GCSE exams and gaining essential qualifications. Finally, Key Stage 5 offers advanced studies for ages 16-18, paving the way for university or career opportunities.
Edumentors’ online tutoring platform, offers professional tutors who can guide students through these stages. With personalised support, students can strengthen their skills, build confidence, and overcome challenges. This extra help ensures they stay on track and achieve their full potential. By combining the UK education system’s structure with expert tutoring, students gain the tools they need for lifelong success.








