The bus stop method is a simple and effective way to teach division, widely used in Key Stage 2. It helps children break down large numbers into smaller steps, making division easier to understand. Many students struggle with division, but this method provides a clear structure that builds confidence and accuracy. Just as the part-whole model helps younger children visualise number relationships, the bus stop method gives older students a concrete framework for tackling division.
This guide will explain how to do the bus stop method, step by step. You’ll also find bus stop method examples, practise questions, and bus stop division worksheet recommendations to support your child’s learning. By the end, you’ll have all the tools you need to help your child master division.
What Is the Bus Stop Method?
The bus stop method is a straightforward way to divide numbers, it’s a type of short division that breaks calculations into clear steps. The method gets its name from the way the numbers are arranged. The dividend (the number being divided) is placed under a long division symbol, while the divisor (the number dividing) sits outside. This setup resembles a bus stop, making it easier for children to visualise and remember.
Schools use this method because it helps children improve their mental maths and get ready for harder division. Learning it makes problem-solving easier, builds confidence, and prepares them for more advanced maths in the future.
How to Do the Bus Stop Method?
The process of bus stop method follows a simple, step-by-step process to make division easier. Once children understand the setup, they can break down even large numbers into smaller, manageable steps. Here’s how it works:
Setting Up the Division Problem
Start by writing the number being divided (dividend) under the long division symbol. Place the number you are dividing by (divisor) outside. This setup looks like a bus stop, which is why the method gets its name.
For example, let’s solve 96 ÷ 4 using the bus stop method:
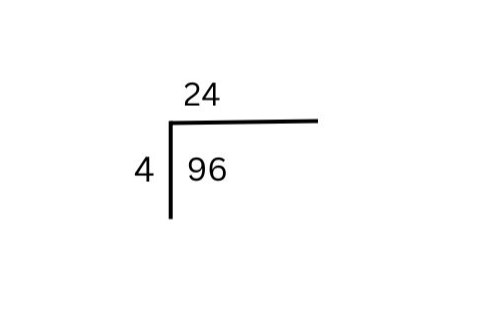
1) Start with the first digit (9). Ask: “How many times does 4 fit into 9?” The answer is 2 (because 4 × 2 = 8). Write 2 above the line. Subtract 8 from 9, leaving 1.
2) Carry the remainder (1) over to the next digit (6), making it 16.
3) Divide 16 by 4. The answer is 4 (because 4 × 4 = 16). Write 4 above the line.
4) No remainder is left, so the final answer is 24.
Dividing Each Digit in Order
Always start with the leftmost digit of the dividend and work your way to the right. If the divisor doesn’t fit exactly, carry over the remainder to the next digit.
Handling Remainders Correctly
Sometimes, division won’t result in a whole number. In this case, the remainder can be:
- Left as a whole number (e.g. 98 ÷ 5 = 19 remainder 3).
- Written as a fraction (e.g. 98 ÷ 5 = 19⅗).
- Converted into a decimal by continuing the division process.
The Importance of Knowing Times Tables
To use the bus stop method effectively, children need strong times tables knowledge. Knowing multiplication facts helps them divide quickly and reduces mistakes. Regular practice will make solving division problems much easier.
Long Division vs. the Bus Stop Method
Both long division and the bus stop method are used to divide numbers, but they work in slightly different ways. Understanding the difference can help parents guide their children in choosing the right method for each problem.
What’s the Difference?
The bus stop method is a short division technique. It’s quicker and easier because it breaks down the division into smaller steps without requiring extra written calculations. Children follow a simple process, dividing one digit at a time and carrying over remainders if needed.
Long division, on the other hand, is a more detailed approach. It involves additional steps, including multiplication and subtraction at each stage. This method is typically used for more complex division problems, especially when dividing large numbers or working with decimals.
When Should Each Method Be Used?
Bus Stop Method – Best for smaller numbers and when the divisor is a single-digit number. It’s quick, efficient, and perfect for mental maths practice.
Long Division – Used when dividing by larger numbers or when a problem requires a more detailed breakdown. It’s essential when working with two-digit divisors or finding exact decimal values.
Why Is the Bus Stop Method More Suitable for Key Stage 2?
For Key Stage 2 maths, the bus stop method is the preferred choice. It helps children develop confidence in division before moving on to more complex calculations. Since it’s simpler and easier to remember, it allows children to focus on getting the correct answer without being overwhelmed by too many steps.
How to do Bus Stop Method: Examples and Questions
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s look at some bus stop method examples to see how it works in practise. These step-by-step examples will help parents explain the method to their children. After that, you’ll find practise questions to reinforce learning.
Bus Stop Method Examples
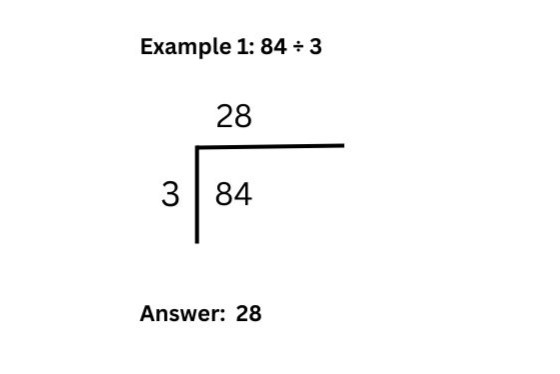
Step 1: Start with 8 (the first digit). How many times does 3 fit into 8? It goes 2 times (3 × 2 = 6). Write 2 above the 8. The remainder is 2.
Step 2: Carry over the remainder 2 to the next digit, making 24. How many times does 3 fit into 24? The answer is 8 (3 × 8 = 24). Write 8 above the 4.
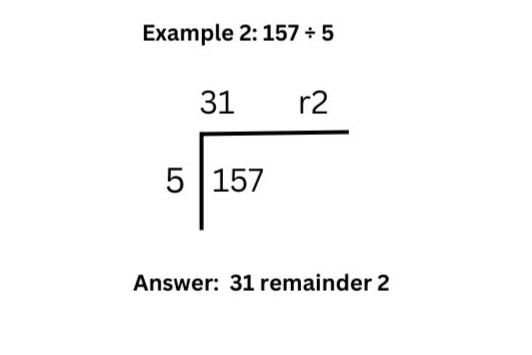
Step 1: 5 doesn’t fit into 1, so move to 15. How many times does 5 fit into 15? The answer is 3 (5 × 3 = 15). Write 3 above the 15.
Step 2: Move to the next digit (7). How many times does 5 fit into 7? It goes 1 time (5 × 1 = 5). Write 1 above the 7.
Step 3: There’s a remainder of 2, which we write as r2 (remainder 2).
Bus Stop Method Questions
Now it’s time to practise. Start with easy questions, then move to more challenging ones.
Easy Questions:
- 48 ÷ 4 = ?
- 72 ÷ 6 = ?
- 125 ÷ 5 = ?
Intermediate Questions:
- 238 ÷ 7 = ?
- 312 ÷ 6 = ?
- 427 ÷ 8 = ?
Challenging Questions:
- 1,023 ÷ 9 = ?
- 1,546 ÷ 7 = ?
- 2,305 ÷ 4 = ?
Encourage your child to show their working and double-check answers. The more they practise, the more confident they’ll become.
Bus Stop Method – Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even though the bus stop method is a simple way to divide numbers, children can still make mistakes. Understanding these common errors and knowing how to fix them can make a big difference in their learning.

1. Misplacing Numbers in the Setup
One of the most common mistakes is writing the numbers in the wrong place. If the divisor or dividend isn’t set up correctly, the whole calculation will be incorrect.
Tip: Remind your child that the dividend always goes inside the bus stop, while the divisor sits outside. Double-check the setup before starting the division.
2. Forgetting to Carry Remainders
Many children forget to carry remainders when moving from one digit to the next. This can lead to incorrect answers.
Tip: Encourage them to write down the remainder clearly and bring it down to the next digit before continuing. If needed, they can lightly circle or underline remainders to keep track.
3. Skipping Steps or Making Calculation Errors
Sometimes, children rush through the steps or miscalculate the number of times the divisor fits into the dividend. This often happens when they aren’t confident with their times tables.
Tip: Make sure they take their time and double-check each step before moving on. Practising multiplication facts regularly can also help them divide more quickly and accurately.
4. Struggling with Remainders
Some children don’t know what to do with a remainder at the end of a calculation. Should they leave it as a whole number, convert it into a fraction, or continue with a decimal?
Tip: Explain that the answer depends on the type of question. If dividing objects (e.g. sweets between friends), a remainder is fine. If dividing money or measurements, converting it into a decimal may be more useful.
Building Good Habits
Mistakes are a normal part of learning, but with practise and the right strategies, children can become confident in using the bus stop method. Encouraging them to check their work, take their time, and use clear steps will help them avoid these common errors.
Helpful Resources for Practising the Bus Stop Method
To help your child get better at bus stop division, it’s useful to have the right resources. Here are some free and easy-to-use tools to support their learning.
Printable Worksheets
Worksheets provide structured practice and allow children to build confidence step by step. You can find free printable division worksheets online that include:
- Basic division questions for beginners.
- Progressive difficulty levels (starting with smaller numbers and moving to larger ones).
- Word problems to help children apply division in real-life situations.
Where to find them? you can find them on websites such as: BBC Bitesize, Corbettmaths or Primary Resources
Online Division Games
If your child enjoys digital learning, interactive games can make division practise more engaging. Many educational websites offer bus stop method games that:
- Provide instant feedback on answers.
- Allow children to practise at their own pace.
- Turn learning into fun challenges instead of worksheets.
Recommended Websites: Topmarks (“Division Bingo” and “Hit the Button” for times tables) , Math Playground (interactive division games) and BBC Bitesize (animated division lessons).
Using these free resources, parents can support their child’s learning and make bus stop division feel more natural and less stressful.
Conclusion
The bus stop method is a simple yet powerful way to help children master division. It breaks down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps, making division easier to understand. Since it’s widely taught in Key Stage 2 maths, ensuring your child is confident with this method will support their overall progress in maths. As your child progresses to Year 7 maths, they’ll need to apply these division skills to more complex problems.
If your child needs extra support, consider using online KS2 tutors who can provide personalised guidance. A tutor can explain tricky concepts, give one-on-one feedback, and help boost confidence in maths. Good Luck!
You Might Find Interesting
What Are SATs? A Complete Guide for Parents
FAQs:
What is bus stop method?
The bus stop method is a quick, written method for long division. You write the number being divided (the dividend) under a bracket that looks like a bus stop, and the number you’re dividing by (the divisor) outside. You then divide digit by digit from left to right, carrying remainders to the next column and building the answer (the quotient) above the bracket.
How to do the bus stop method?
- Write the divisor outside and the dividend inside the “bus stop”.
- Divide the first digit(s); write the result above.
- Carry any remainder to the next digit.
- Repeat until all digits are used.
- If needed, write a remainder (or continue with decimals).
Example: 496 ÷ 4
- 4 into 4 = 1 (write 1).
- 4 into 9 = 2 remainder 1 (carry 1 to make 16).
- 4 into 16 = 4.
Answer: 124.
How to do bus stop method with 2 digits?
The idea is the same, but you divide by the whole 2-digit number each step and may need short multiplication to check fits.
Example: 1,274 ÷ 26
- Set up: 26 ) 1274.
- 26 doesn’t go into 1 or 12, so use 127.
- 26 × 4 = 104, 26 × 5 = 130 (too big) → write 4 above the 7; subtract 127 − 104 = 23.
- Bring down the next digit (4) → 234.
- 26 × 9 = 234 exactly → write 9.
Answer: 49.
If it isn’t exact, write the remainder (e.g., “r 7”) or continue by adding a decimal point and zeros to the dividend and keep dividing.