GCSE Physics – Everything You Need to Know
GCSE Physics, a subject as expansive and intriguing as the universe itself, can be daunting yet deeply rewarding. This guide simplifies the complexities of the GCSE Physics syllabus, making it accessible and engaging for both students and parents. Covering essential topics such as the GCSE Physics marking and grading schemes, key concepts, and common challenges, it also offers insights into effective revision strategies, including the use of past papers and many more tips.
Overview of the GCSEs
GCSEs are widely recognised qualifications in the UK, typically taken by students aged 14 to 16. As a parent, you are likely already somewhat familiar with this important academic milestone.
Each student chooses a selection of subjects to study, with Physics being a part of the Science suite. This phase of their educational journey allows them to delve deeper into specific areas of interest and sets the foundation for A-Levels, further education, and even career paths.
Physics, considered one of the three core sciences, is a fascinating subject that probes into the nature of the universe, from the smallest particles to the grand scale of space itself. Studying GCSE Physics equips students with a rigorous understanding of the principles that govern the world around us, while fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills that are invaluable in various walks of life. It’s not just for future Einsteins – GCSE Physics can open doors to a wide range of academic and career opportunities.
The GCSE Grading Scheme
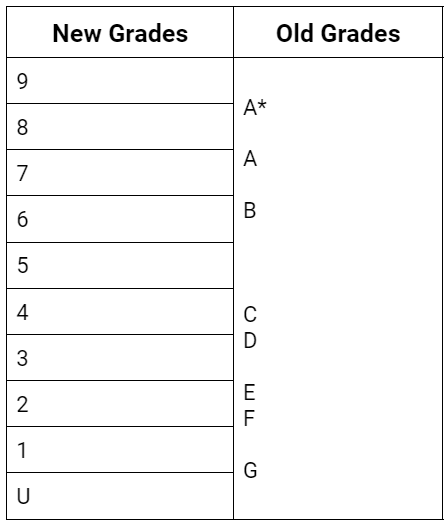
The GCSE grading scheme employs a numerical system from 1-9, replacing the old A-G scale. Grade 9 is the highest, signifying exceptional achievement, while 1 is the lowest pass grade. Grades 9, 8 and 7 correspond to the old top grades of A and A, indicating a high level of understanding of the subject. Grades 6, 5, and 4 are comparable to B and C grades, considered a standard pass. Anything below grade 4 indicates areas for improvement.
In the context of GCSE Physics, achieving a strong grade demonstrates a student’s solid grasp of complex scientific concepts and their ability to apply this knowledge, both of which are highly valued in further studies and the world of work.
Key Topics in GCSE Physics
Force and Motion
This topic explores the rules that govern how objects move and interact in the universe. From scalar and vector quantities to Newton’s laws of motion, students gain a fundamental understanding of the forces acting on an object in motion.
Energy
Energy, an integral concept in physics, is addressed in this section. Students learn about the different forms of energy, energy transfers and transformations, along with the critical principle of conservation of energy. Learn more about Energy.
Waves
Properties and Behaviour of Waves
The fascinating world of waves comes alive here as students delve into wave speed, reflection, refraction, diffraction, and superposition.
Applications of Waves
This section also explores how waves find application in different areas of life and technology.
Electricity and Magnetism
Principles of Electric Circuits and Magnetic Fields
Here, the focus is on understanding the workings of electric circuits, circuit components, and the laws that govern magnetic fields.
Practical Aspects of Electricity
Students also gain practical knowledge about the domestic use of electricity, its safety measures, and how electricity interacts with magnetism. Learn more about Electricity.
Atomic Structure
Understanding the Atom
This section whisks students away to the microscopic world of atoms, where they learn about atomic models and the structure of the atom itself. Learn more about atomic structure.
Radioactivity and Its Implications
Moreover, they explore the concepts of radioactive decay, nuclear fission and fusion, and the real-world applications and dangers of radiation.
Space Physics
The Solar System and Beyond
A thrilling journey through space begins with this topic. Students learn about the Solar System, the life cycles of stars, and the overall structure of the Universe.
The Theory of the Big Bang
They also explore the fundamental theories about the origin of the universe, such as the Big Bang theory.
Each of these sections offers not only an exciting exploration into the laws governing the universe but also presents ample opportunities to develop essential scientific skills. These skills include carrying out experiments, analysing data, problem-solving, and applying theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios, making the GCSE Physics syllabus a holistic learning experience.
Common Difficulties in GCSE Physics

Understanding Abstract Concepts
GCSE Physics often introduces concepts that are not directly observable or intuitive. From quantum phenomena to the curvature of spacetime, these abstract ideas can sometimes pose challenges for students.
Mathematical Skills
Physics is a heavily quantitative science. It requires a strong grasp of mathematics, particularly in areas such as algebra and trigonometry. Some students may find the mathematical aspect of physics daunting.
Practical Experimentation
Understanding Experimental Procedures
Physics isn’t just about theory; it’s also about practical experimentation. The design, setup, and execution of experiments can be complex, and some students may struggle with these aspects.
Interpreting Experimental Results
Additionally, interpreting and analysing experimental results, particularly when they don’t align with theoretical expectations, can also be challenging.
Exam Technique
Time Management
In exams, time management is often a struggle. Completing all questions in the allocated time while maintaining accuracy can be demanding.
Application of Knowledge
Another difficulty is applying learned concepts to new or unfamiliar situations presented in exam questions. This requires a deep understanding of the subject and the ability to think critically.
Understanding these common difficulties can help parents and students identify potential areas of struggle early on, and seek appropriate help, such as through additional resources or targeted tuition.
Sample GCSE Physics Exam Questions and Explanations
Question 1: Force and Motion
Question: An object of mass 2 kg is accelerating at 3 m/s². What is the force acting on it?
Answer: 6 N.
Explanation: Force (F) can be calculated using Newton’s second law of motion, which states that Force equals mass (m) times acceleration (a), or F = m*a. So, 2 kg * 3 m/s² equals 6 N.
Common Mistake: Students often forget to apply Newton’s second law correctly or mix up the units.
Question 2: Energy
Question: What type of energy is stored in a stretched spring?
Answer: Elastic potential energy.
Explanation: When a spring is stretched or compressed, it stores elastic potential energy. This energy can be released when the spring is allowed to return to its original shape.
Common Mistake: Confusing different types of potential energy – gravitational, chemical, and elastic.
Question 3: Waves
Question: What is the term for the bending of waves around obstacles?
Answer: Diffraction.
Explanation: Diffraction is the phenomenon of waves bending around obstacles or spreading out after passing through narrow openings. It occurs with all types of waves, including light, sound, and water waves.
Common Mistake: Students often confuse diffraction with refraction, which is the bending of waves due to a change in speed when moving from one medium to another.
Question 4: Electricity and Magnetism
Question: In an electrical circuit, what component is used to measure current?
Answer: Ammeter.
Explanation: An ammeter is an instrument used in a circuit to measure electric current. It is always connected in series with the component of interest.
Common Mistake: Students sometimes confuse an ammeter with a voltmeter, which is used to measure potential difference (voltage) and is connected in parallel.
Question 5: Atomic Structure
Question: What are isotopes?
Answer: Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Explanation: The atomic number (number of protons) defines an element, but the number of neutrons can vary, creating isotopes. This difference in neutron number results in isotopes of the same element having different atomic masses.
Common Mistake: Many students mistake isotopes for ions, which are atoms with an unequal number of protons and electrons, thus bearing a charge. Isotopes, on the other hand, are neutral.
Overview of the GCSE Physics Marking Scheme
The GCSE Physics marking scheme is a vital resource for understanding how examiners grade student responses. It details the allocation of marks for each question and provides insight into what constitutes a high-quality answer.
Component Breakdown
The GCSE Physics exam typically consists of two components:
- Multiple-Choice Questions – These are direct questions where students select the correct answer from a list of options. Each correct answer generally receives one mark.
- Structured Questions – These include short answer questions, extended response questions, and practical-based questions. The number of marks varies based on the complexity and depth of the question.
Mark Allocation
Each question in the exam paper indicates the number of marks available. Simple, direct questions may be worth one mark, while more complex questions requiring longer, detailed responses can be worth several marks.
Quality of Written Communication
For questions involving extended writing, some marks are often allocated for the quality of written communication. This includes clarity of expression, the structure of arguments, and the presentation of information, mathematical calculations, and diagrams.
Practical Skills Assessment
Given the significant emphasis on practical skills in GCSE Physics, certain questions are specifically designed to assess these skills. These questions can cover areas such as the ability to select and use appropriate equipment, make accurate observations, handle data, and interpret experimental results.
Understanding the GCSE Physics marking scheme can help parents guide their children in exam technique and preparation, ensuring they know where to focus their efforts and how to best structure their answers.
Effective Revision and Study Resources for GCSE Physics
Studying for GCSE Physics can be a challenging endeavour, but with the right resources and revision strategies, students can achieve success. Here are some of the best tools and techniques available:
Textbooks and Revision Guides
Many publishers produce textbooks and revision guides specifically tailored to the GCSE Physics syllabus. These books often include detailed explanations of concepts, worked examples, and practice questions.
Online Platforms
There are several online platforms that provide extensive resources for GCSE Physics. These include:
- BBC Bitesize: Offers a wide range of learning resources, including interactive content, quizzes, and revision notes.
- Physics and Maths Tutor: Provides past papers, revision notes, and worksheets.
- Seneca Learning: An interactive learning platform that uses cognitive science techniques to enhance learning and retention.
Apps
Several educational apps can aid revision on-the-go. Apps like Gojimo and Revision Buddies contain thousands of GCSE Physics questions, flashcards, and notes.
Past Papers and Mark Schemes
Regularly working through past papers is one of the most effective ways to revise. It can help students familiarise themselves with exam format, question styles, and timing. Here are GCSE Physics past papers.
YouTube Channels
Channels such as FreeScienceLessons, PhysicsOnline, and Primrose Kitten offer video tutorials covering the GCSE Physics syllabus. These videos can help visual learners grasp complex concepts.
Tutoring Services
Tutoring can provide personalised support and resources tailored to a student’s individual learning style and areas of difficulty.
The resources listed above can be particularly helpful, but it’s important for students to identify which methods work best for them. A combination of different resources often results in the most effective revision.
The Benefits of GCSE Physics Tuition
GCSE physics tutor can enhance a student’s understanding and performance in GCSE Physics. Here are some of the key benefits:
Individual Attention
In a classroom setting, teachers may not be able to provide individual attention to every student. However, with one-on-one tuition, the tutor can focus entirely on one student, providing personalised guidance and support.
Customised Learning Experience
Tutors can tailor lessons to suit the student’s unique learning style and pace. This customisation can be especially beneficial in a subject like Physics, where students may struggle with complex concepts and need to approach them in different ways.
Subject-Specific Expertise
A GCSE Physics tutor will have specific expertise in the subject, allowing them to explain challenging topics in depth and offer insider tips on how to approach exam questions.
Reinforcement of Classroom Learning
Tuition sessions can complement classroom learning by reinforcing what the student has learnt at school, addressing any misunderstandings or gaps in knowledge, and providing additional practice with difficult concepts. Learn here what makes a good tutor.
Boosting Confidence
By addressing areas of difficulty and providing regular feedback, tuition can help students build confidence in their physics abilities, reducing exam stress and increasing motivation to learn.
Flexibility
Private tuition offers flexibility, as sessions can be arranged at times that suit the student, allowing for a balanced schedule of school, extracurricular activities, and rest.
In addition to these benefits, online tutoring brings a few more advantages:
Convenience
Online tuition eliminates travel time and allows students to learn from the comfort of their home, making it a highly convenient option.
Access to Resources
Online tutoring platforms often come with a range of additional resources, such as interactive quizzes, videos, and digital textbooks, which can greatly aid revision.
Global Reach
Online tuition is not limited by geography, meaning students can have access to highly qualified tutors, regardless of their location.
Tutoring, and specifically online tutoring, can provide significant advantages, particularly for a challenging subject like GCSE Physics. By choosing the right tutor, students can gain not just a better understanding of physics, but also improved overall academic skills and confidence.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricacies of GCSE Physics can be a formidable challenge, yet one that paves the way for a bright and exciting future in fields as diverse as engineering, astrophysics, medicine, and beyond. However, with the right guidance, tools, and an unwavering commitment to understanding, this challenge can transform into an opportunity — a stepping stone to future academic and professional success.
Unlike traditional tutoring services, Edumentors’ GCSE Physics tutors operate seamlessly online, allowing your child to learn from the best, regardless of geography. This platform not only aids in mastering the GCSE Physics syllabus but also instils a deep, enduring understanding of the subject. Such an understanding can ignite a passion for learning, empower your child with newfound confidence, and open doors to a world of possibilities in science.